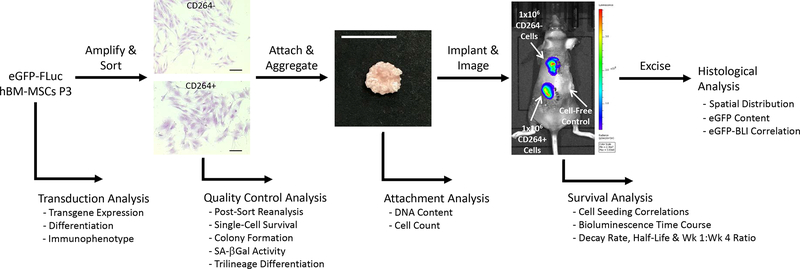
Figure 1.
Overview of project design to quantify the in vivo survival of aging CD264+ hBM-MSCs. Following lentiviral transduction, hBM-MSCs were evaluated for transgene expression and stem cell fitness. eGFP-FLuc hBM-MSCs were amplified and then sorted into CD264+ and control CD264− populations. Quality control assessment of CD264-sorted cells evaluated sort purity, aging phenotype and single-cell survival. Attachment of CD264+ and CD264− eGFP-FLuc hBM-MSCs to HA/TCP porous scaffolds was quantified, and then seeded scaffolds were aggregated with mouse thrombin and fibrinogen. Aggregated hBM-MSC constructs were implanted subcutaneously on the dorsal surface of immunodeficient mice, and bioluminescence imaging was performed every 3–4 days for 31 days. Bioluminescent signal was used to determine the survival kinetics of CD264-sorted hBM-MSCs. On the final day of imaging, implants were excised for histological analysis. Scale bars: 200 μm (cells); 1 cm (construct). Abbreviations: BLI: bioluminescence imaging; eGFP: enhanced green fluorescent protein; FLuc: firefly luciferase; HA/TCP: 15% hydroxyapatite/85% β-tricalcium phosphate; hBM-MSCs: human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; P3: passage 3; SA β-Gal: senescence-associated β-galactosidase.