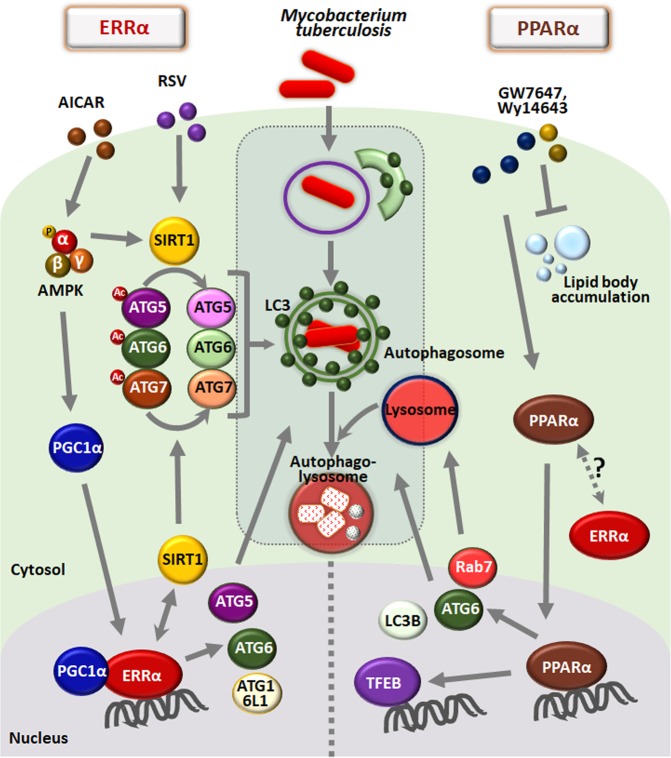
Fig. 2. The roles of ERRα and PPARα in autophagy and host defense against Mtb infection.
(Left) ERRα, which is induced by either AMPK or SIRT1 activation, contributes to the induction of autophagosome formation in BMDMs. ERRα is required for the transcriptional activation of several ATGs containing ERR response elements in the promoters. In addition, the cooperation of ERRα with SIRT1 promotes the deacetylation of ATG5, ATG6, and ATG7, thereby activating autophagy at the posttranslational level. ERRα-mediated autophagy activation results in increased phagosomal maturation and antimicrobial responses during Mtb infection. (Right) PPARα, which is activated by PPARα ligands (GW7647 and Wy14643), contributes to enhanced autophagosomal formation and maturation in BMDMs. PPARα is essential for the transcriptional activation of several ATGs, TFEB and lipid catabolism. PPARα reinforces antimicrobial responses to mycobacterial infection by inducing autophagic maturation, TFEB, and lipid catabolism. AICAR, 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide 1-β-D-ribofuranoside; RSV resveratrol