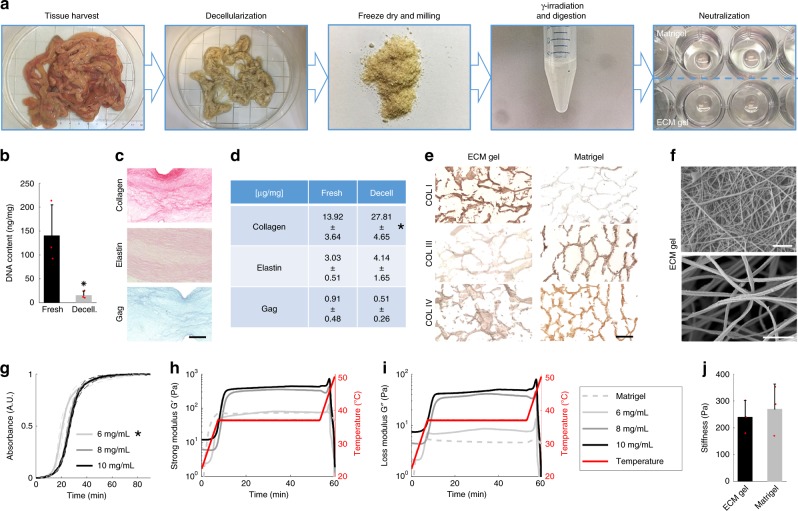
Fig. 1. Extracellular matrix hydrogel characterization.
a The gelation preparation protocol consists of decellularization of the SI mucosa/submucosa, freeze-drying process, milling into a fine powder, gamma-irradiating and digesting the powder in pepsin and HCl for 72 h, and neutralization to a physiological pH, salinity and temperature. b DNA quantification in fresh (immediately after organ harvest) and decellularized piglet mucosa. Mean ± S.D. (n = 3 small intestines). Two-sided t-test *P < 0.05. Asterisk denotes significance. Red dots show individual data points. c Histological sections of fixed ECM gel drops stained with Picrosirius Red, Verhoeff’s and Alcian Blue for collagen, elastin and glycosaminoglycans, respectively. Scale bar 200 μm. d Quantification of ECM proteins: collagen, elastin and GAG. Mean ± S.D. (n = 3 gel batches). Two-sided t-test *P < 0.05. e Analysis of the collagen types in ECM gel and Matrigel by staining for collagen I, III, and IV. Scale bar 100 μm. f Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the ECM gel displaying the interconnected fibrous network. Scale bars 1 µm. g Spectrophotometry used to assess the turbidity of the samples during gelation. Mean ± S.D. (n = 2 gel batches). Two-sided t-test *P < 0.05 of Tlag. h, i Oscillatory rheology provides a rheological profile of various concentrations of the ECM gel and Matrigel, for both h storage modulus and i loss modulus. j Elastic modulus measured by nanoindentation of 6 mg/mL ECM gel vs. Matrigel in 30 µL drops. Mean ± S.D. (n = 3 gel droplets). Two-sided t-test *P < 0.05.