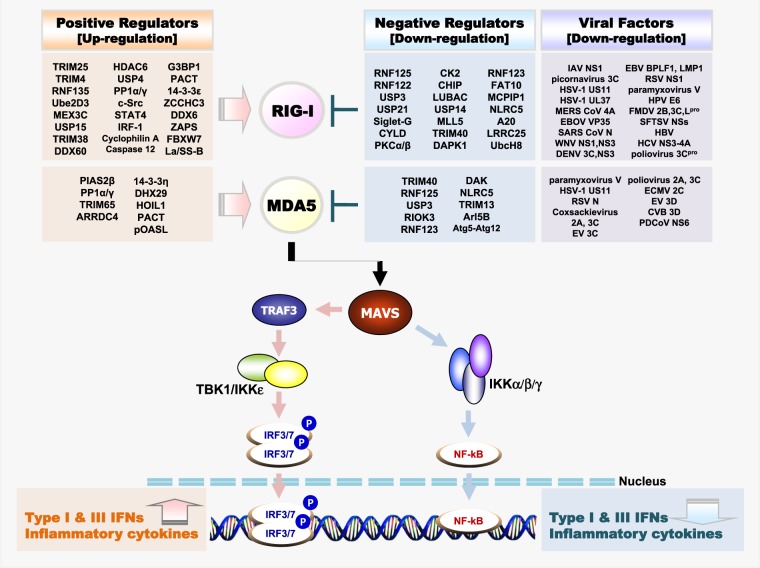
Fig. 1. Regulators and interacting viral proteins of the RLR–MAVS antiviral signaling pathway.
Schematic presentation of positive and negative regulators of RLRs (Top) and melanoma differentiation-associated protein-5 (MDA5) (Bottom) through PTMs or non-PTMs and immune invasion viral proteins interacting with RIG-I (Top) and MDA5 (Bottom). The RLR-MAVS pathway includes the key cytosolic sensors RIG-I and MDA5, which detect viral RNA. These sensors subsequently interact with the central antiviral signaling protein MAVS, which in turn activates the transcription factors NF-κB and IRF3/IRF7 via the cytosolic kinases IKK and TBK1/IKKε, respectively. Activated transcription factors NF-κB, IRF7 and IRF3 translocate to the nucleus and induce transcription of type I IFN and pro-inflammatory genes