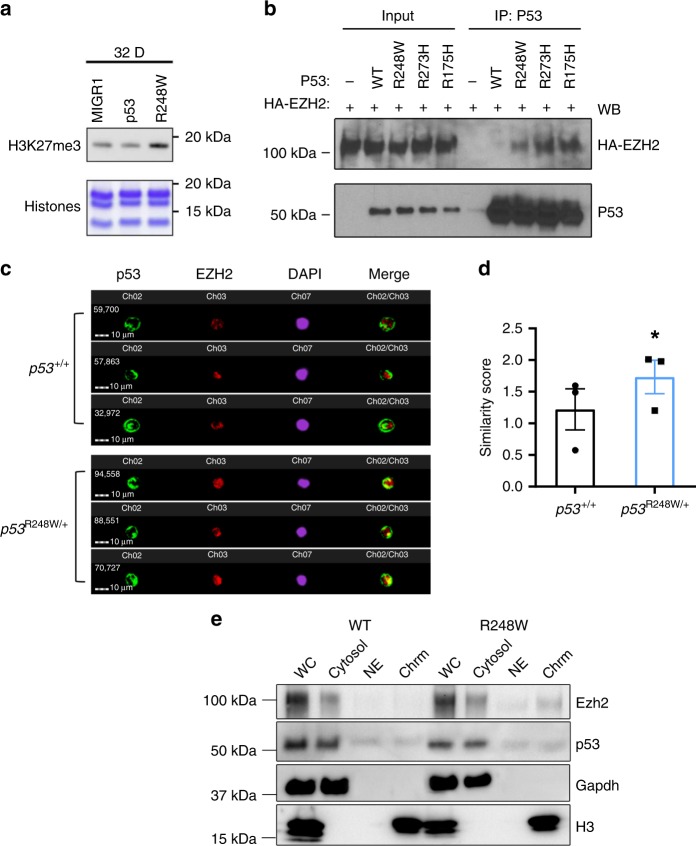
Fig. 5. Mutant p53 enhances the association of EZH2 with the chromatin in HSPCs.
a 32D cells expressing mutant p53, but not wild-type (WT) p53, displayed increased levels of H3K27me3 as determined by immuno-blot analysis. b Several mutant p53 proteins, but not wild-type p53, show enhanced association with EZH2 as assayed by co-IP (co-immunoprecipitation) experiments. c Mutant p53 and EZH2 localization in HSPCs (Lin−Sca1+Kit+CD150+) as determined by ImageStream flow cytometry analysis. d Quantification of p53 and Ezh2 co-localization in the nucleus of HSPCs (Lin−Sca1+Kit+CD150+). A similarity feature determined the amount of overlay between p53 and Ezh2 within the DAPI mask. The higher the similarity score is, the more co-localized staining is within the nucleus; n = 3 biological replicates. e Cellular fractionation shows increased EZH2 association with the chromatin fraction in p53 mutant HSPCs. The absence of Gapdh (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) and exclusive distribution of histone H3 in the chromatin fraction indicates no cross contamination between different cellular compartments. WC whole cell extract, Cyto cytosol, NE nuclear cytosol, Chrm chromatin. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. P-values were calculated using paired t-test in d; *P < 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.