Figure 1.
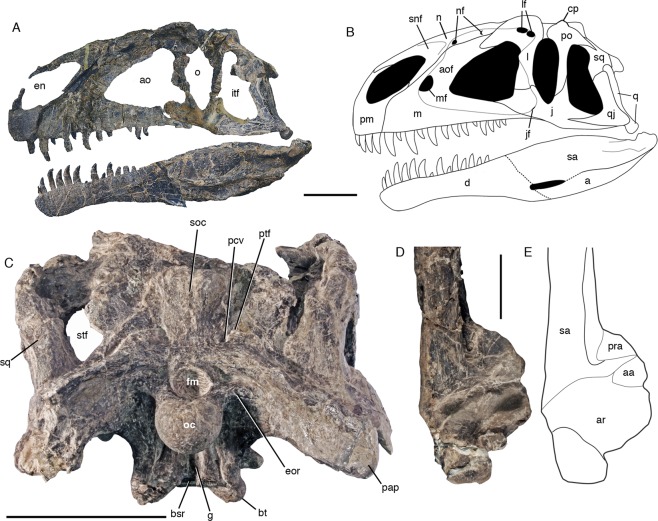
Cranial anatomy of Asfaltovenator vialidadi, MPEF PV 3440. (A) composite reconstruction of the skull and lower jaws, based on disarticulated cranial elements. (B), graphic reconstruction of articulated skull. (C), braincase in occipital view. (D,E) posterior end of left mandible in dorsal view; (D) photo; (E) outline drawing. Abbreviations: a, angular; aa, antarticular; ao, antorbital fenestra; aof, antorbital fossa; ar, articular; bsr, basisphenoid recess; bt, basal tubera; cp, cornual process; d, dentary; en, external nares; eor, exoccipital ridge; fm, foramen magnum; g, groove; itf, infratemporal fenestra; j, jugal; jf, jugal foramen; l, lacrimal; lf, lacrimal fenestrae; m, maxilla; mf, maxillary fenestra; n, nasal; nf, nasal foramina; o, orbit; oc, occipital condyle; pap, paroccipital process; pcf, posterior exit of mid-cerebral vein; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pra, prearticular; ptf, posttemporal foramen; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; sa, surangular; snf, supranarial fossa; soc, supraoccipital; sq, squamosal; stf, supratemporal fenestra. Scale bars are 10 cm (A–C) and 5 cm (D,E).