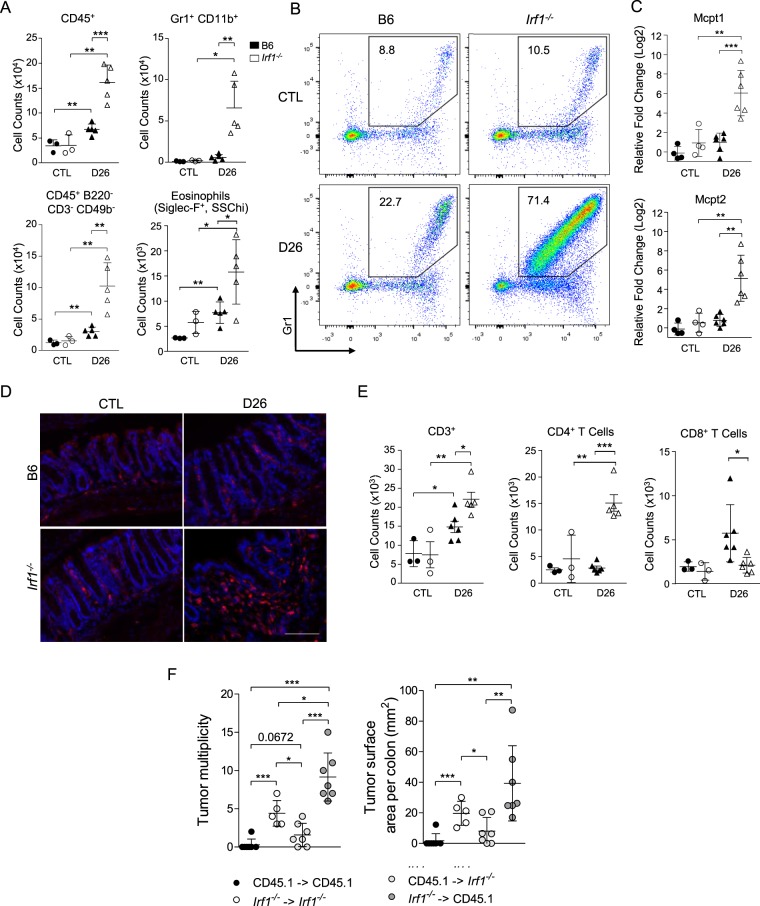
Figure 5.
Elevated leukocytes infiltration in the colon of Irf1−/− mice in response to AOM/DSS. Colon single cell suspensions from control and from treated (D26) B6 (filled symbols) and from Irf1−/− mutants (empty symbols) were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Total counts of CD45+ cells, CD45+ B220/CD3/CD49b lineage negative cells, Gr1+ CD11b+ cells, and Siglec F+ cells are shown for individual mice along with means ± SD (n = 3 for CTL, n = 5 for B6 D26 and Irf1−/− D26); Statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student’s t-tests (*<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001). (B) Representative FACS plots of Gr1+ CD11b+ cells. Numbers indicate mean % of myeloid cells using the gating window shown. (C) Relative expression of the mast cell markers Mcpt1 and Mcpt2 in the colon colons of control and treated B6 (n = 4) and Irf1−/− mutants (n = 6) measured by qRT-PCR. (D) Representative images of Immunofluorescence staining for Cd11b+ myeloid (red) in the colon of control and treated mice, with control nuclear DNA stain DAPI (blue); Scale bars indicate 100 μm. (E) Total counts of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells are shown for individual mice along with means ± SD (n = 3 for CTL, n = 5 for B6 D26 and Irf1−/− D26); Statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student’s t-tests (* < 0.05, ** < 0.01, ***<0.001). (F) Susceptibility to CA-CRC in bone marrow chimeras (n = 7 for CD45.1 - >CD45.1, CD45.1 - > Irf1−/−, Irf1−/– > CD45.1, n = 6 for Irf1–/ - > Irf1−/−) measured as tumor multiplicity and total tumor surface area. Mice were injected ip with AOM (7 mg/kg) once followed by three cycles of 2% (w/v) DSS exposure (4 days each) and sacrificed 6 weeks after the final DSS treatment. Statistical significance of inter-group differences was assessed using unpaired Student’s t-tests (*<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001).