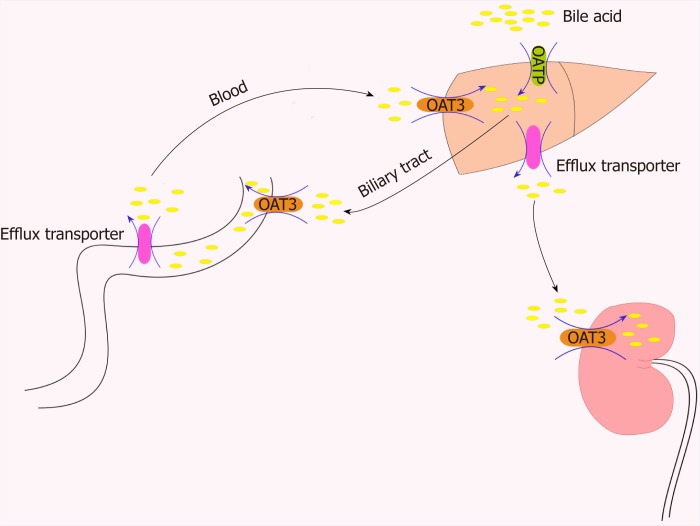
Figure 2.
Role of organic anion transporters/organic anion transporter polypeptides in the transport of bile acids through the “intestinal-liver-kidney” axis. In order to maintain the important physiological process of enterohepatic circulation of bile, hepatocytes recover bile acids from portal vein blood through certain members of the organic anion transporter polypeptide family (e.g., OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and OATP2B1). OAT3 plays a central role in the movement of bile acid through the “intestinal-liver-kidney” axis and is involved in the absorption, metabolism, and excretion of bile acids. OAT: Organic anion transporters.