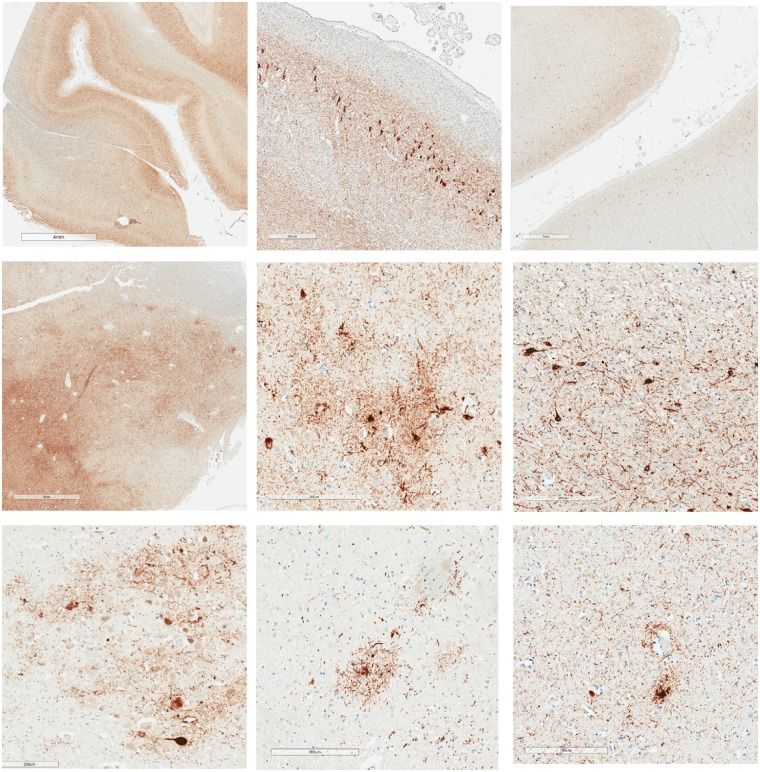
Figure 1.
P-tau accumulates with ageing and in neurodegenerative diseases in diverse brain regions including depths of cortical sulci, in hippocampus, amygdala, mammillary bodies, thalamus, locus coeruleus, raphe nucleus, and around small blood vessels. Images of p-tau accumulations from three males with no known history of TBI, repetitive neurotrauma, or participation in contact or collision sports (Iverson et al., 2019) (Cases 2, 3, and 5). Case 2 was an 82-year-old male who was not reported to be cognitively impaired at the time of death. He might have had mental health problems at some point during later adulthood, although this was not clearly documented. His cause of death was aortic valve stenosis. His APOE genotype was ε4-3. This case was rated as Braak NFT stage V, Thal amyloid-β phase 3-4, with moderate CERAD neuritic plaques, and NIA-AA designation A3B3C2. Case 3 was an 80-year-old male who was not reported to be cognitively impaired at the time of death. His cause of death was cardiomyopathy. His APOE genotype was ε3-3. This case was rated as Braak NFT stage IV, Thal amyloid-β phase 0, with no CERAD neuritic plaques, and NIA-AA Designation A0B2C0. PART and ARTAG pathology were present. Case 5 was a 73-year-old male who was not reported to be cognitively impaired at the time of death. His cause of death was cardiomyopathy. His APOE genotype was ε3-3. This case was rated as Braak NFT stage IV, Thal amyloid-β phase 1, with sparse CERAD neuritic plaques, and NIA-AA designation A1B2C1. PART and ARTAG pathology were present. Top row: Left = extensive, diffusely distributed p-tau with NFT at low magnification (illustrating uniform involvement of neocortex including sulcal depths that occurs with ageing and with Alzheimer’s disease; scale bar = 4 mm; Case 5, age = 73); middle = CA-2 region of Ammon’s horn with extensive p-tau including NFTs (scale bar = 400 µm; Case 2, age = 82); right = low magnification showing extensive p-tau including NFTs with preferential involvement of neocortical layers 2 and 3 (scale bar = 1 mm; Case 5, age = 73). Middle row: Left = abundant p-tau in amygdala at low magnification (scale bar = 3 mm; Case 5, age = 73); middle = irregularly distributed p-tau involving neurons and astrocytes in amygdala (scale bar = 200 µm; Case 3, age = 80); right = extensive p-tau with NFT involving the mamillary body (scale bar = 200 µm; Case 5, age = 73). Bottom row: Left = p-tau involving the locus coeruleus (scale bar = 200 µm; Case 3, age = 80); middle = p-tau involving the pontine raphe nucleus (scale bar = 200 µm; Case 3, age = 80); right = p-tau within cell processes near a small blood vessel (scale bar = 200 µm; Case 2, age = 82).