Scheme 1.
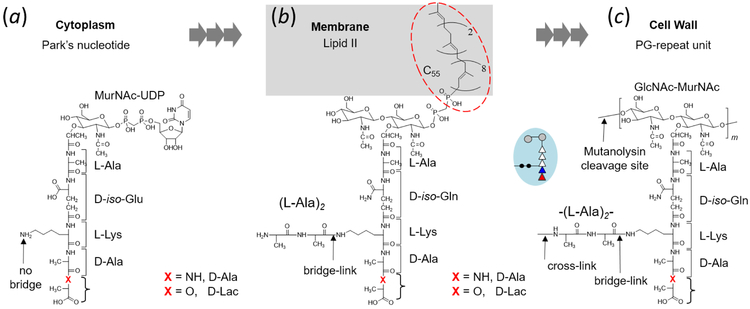
Peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Enterococcus faecalis. (a) The first stage of PG biosynthesis takes place in the cytoplasm with Park’s nucleotide (UDP-MurNAc-l-Ala-D-iso-Glu-l-Lys-d-Ala-d-Ala) as the end product. In vancomycin-resistant E. faecalis, the terminal d-Ala of Park’s nucleotide is replaced by d-Lac. (b) The second stage of PG biosynthesis occurs on the interior side of bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, where UDP-MurNAc-stem from Park’s nucleotide is transported by the lipid transporter C55 to form lipid II (N-acetylglucosamine-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide-pyrophosphoryl-undecaprenol). Attachment of l-Ala-l-Ala bridge to the PG-stem is carried out by peptidyl transferases BppA1 and BppA2. d-iso-Glu is amidated to d-iso-Gln. (c) The final stage of PG biosynthesis is carried out on the external side of cytoplasmic membrane with incorporation of the PG-repeat unit into the cell wall.