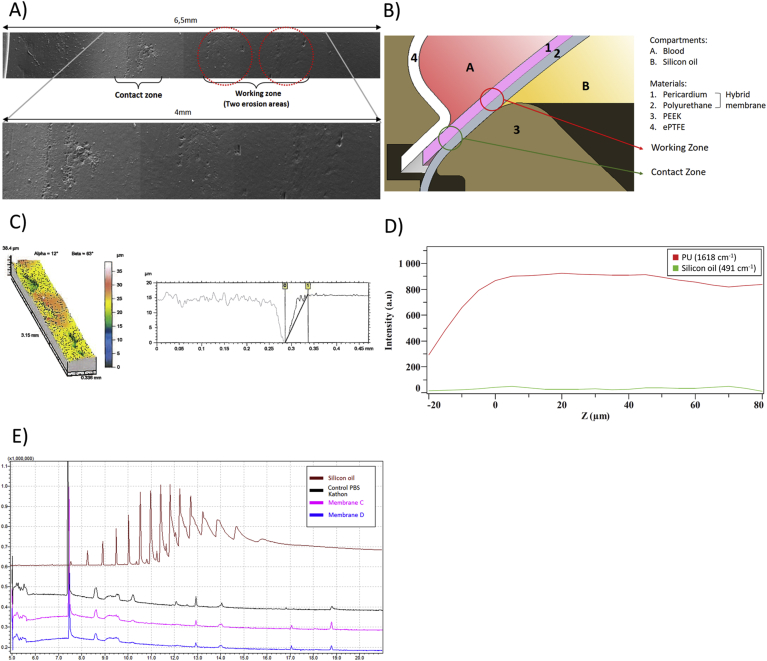
Figure 3.
Surface exploration and permeability. A: Reconstruction using Electronic Microscopic images investigating the two erosion zones on the PU membrane: contact zone on the left corresponding to the zone in contact with the PEEK, and working zone on the right in contact with the oil. B: Cross sectional view of a schematic representation of the disposition of the hybrid membrane inside the C-TAH, with the two erosion areas: the working zone and the contact zone. C: Topographic mapping of the surface of one erosion area on the left, with the topographic profile acquired during exploration of the erosion on the right. D: Raman spectroscopy one membrane, PU wavelengh = 1618 cm−1; silicon oil wavelengh = 491 cm−1, Z profile assessing the absence of silicon oil inside the PU membrane. E: Gas Chromatography coupled with Mass Spectrometry performed on the aging solution of PBS-Kathon used in the endurance bench. Brown: positive control of silicon oil; Black: negative control of non-aged PBS-Kathon; Purple: PBS-Kathon used for the aging of the membrane C; Blue: PBS-Kathon used for the aging of the membrane D.