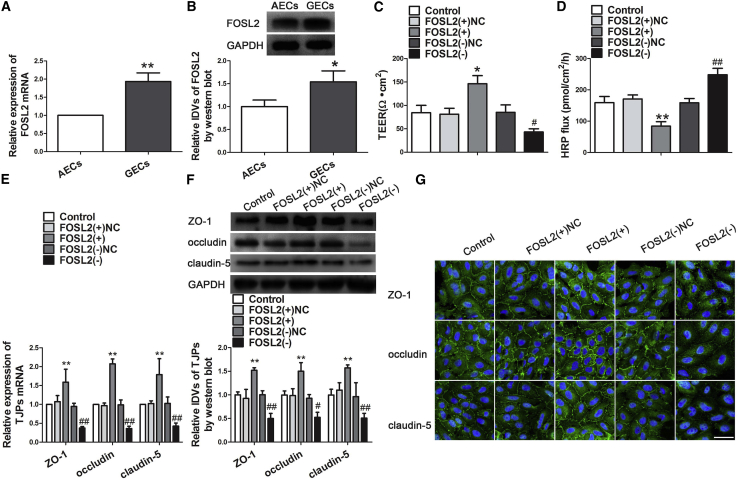
Figure 4.
Knock Down of FOSL2 Increased BTB Permeability and Induced the Expression of Tight Junction-Related Proteins in GECs
(A) Relative expression levels of FOSL2 were detected by quantitative real-time PCR in AECs or GECs. **p < 0.01 versus AECs group. (B) Western blot analysis of FOSL2 in AECs and GECs. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3, each). *p < 0.05 versus AECs group. (C) TEER assay evaluated the effect of FOSL2 on BTB integrity. (D) HRP flux assay evaluated the effect of FOSL2 on BTB permeability. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 5, each). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 versus FOSL2(+)NC group; #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.05 versus FOSL2(−)NC group. (E) The mRNA expression of tight junction-related proteins was detected by quantitative real-time PCR. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3, each). **p < 0.01 versus FOSL2(+)NC group; ##p < 0.01 versus FOSL2(−)NC group. (F) Western blot assay to evaluate the effect of FOSL2 on the protein expression of tight junction-related proteins in GECs. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3, each). **p < 0.01 versus FOSL2(+)NC group; #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 versus FOSL2(−)NC group. (G) Immunofluorescence location of tight junction-related protein in GECs after stable transfection of FOSL2(+), FOSL2(−), and FOSL2-NC. Images are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar, 50 μm.