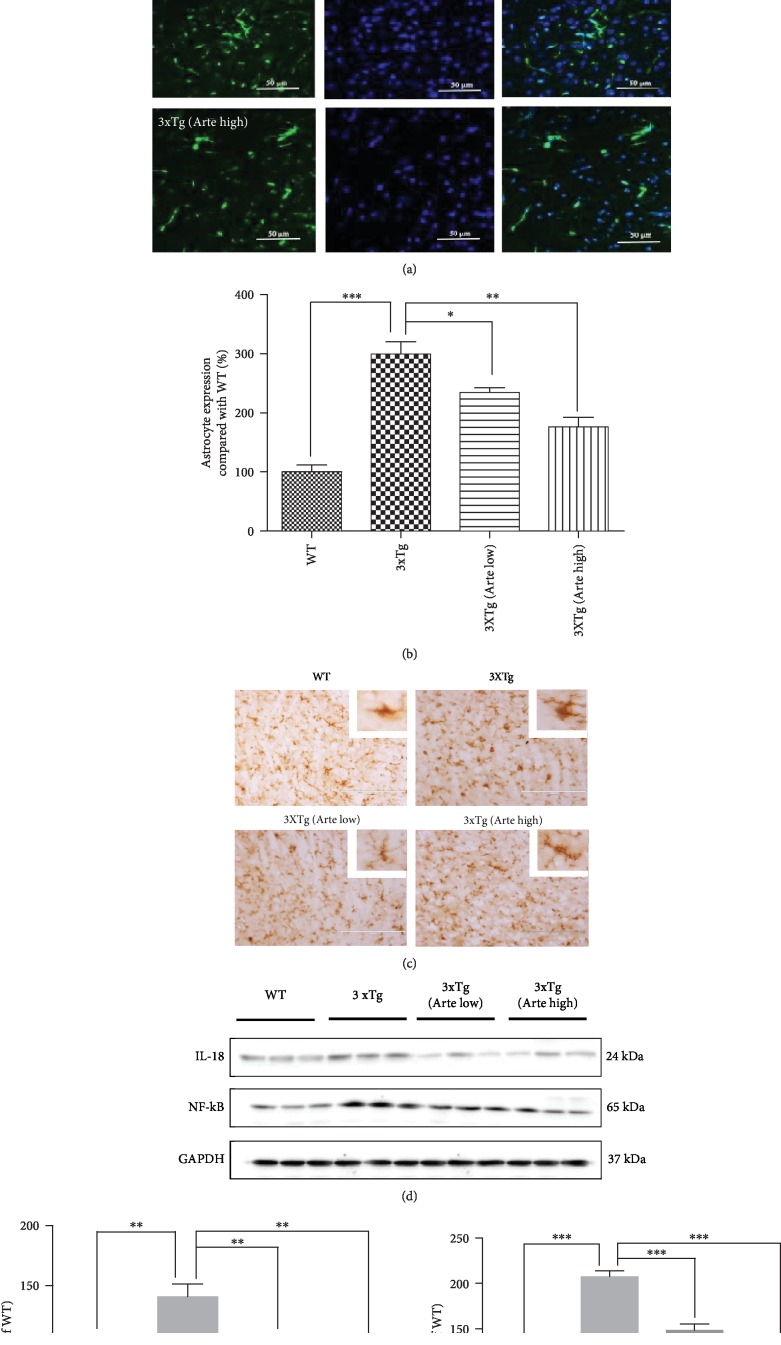
Figure 10.
Artemether treatment attenuated gliosis and expression of inflammatory molecules in the brain cortex of 3xTg-AD mice. Artemether was administered to mice by intraperitoneal injection, once a day, at low doses of 5 mg/kg and high doses of 20 mg/kg, for 4 weeks. Thereafter, the brain cortex slices or extracts of wild-type (WT) compared to 3xTg-AD mice treated with either a low (Arte low) or high dose (Arte high) of Artemether or untreated (3xTg) was submitted for analyses. (a, b) GFAP immunohistochemical expression, scale bar = 50 μm. The histograms in (b) represent the percent count of immunoreactive cells compared to wild-type, in the different experimental groups, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 were considered significantly different. Brain cortex area analyzed for GFAP and Iba-1 expression level was the same as before; five slides per mouse and five mice per treatment group were used for analysis. (c) Iba-1 immunohistochemical expression, scale bar = 200 μm. (d) Western blot analysis of Artemether effect on IL-18 and NF-κB; three mice per treatment group were used for western blot. (e, f) Quantitation of western blots. ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 were considered significantly different.