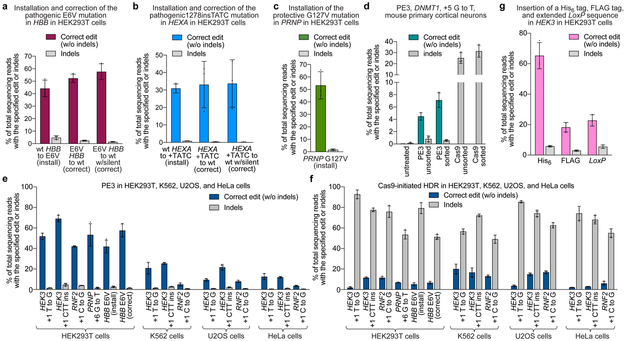
Figure 5. Prime editing of pathogenic mutations, prime editing in primary mouse cortical neurons, and comparison of prime editing and HDR in four human cell lines.
(a) Installation (via T•A-to-A•T transversion) and correction (via A•T-to-T•A transversion) of the pathogenic E6V mutation in HBB in HEK293T cells. Correction either to wild-type HBB, or to HBB containing a PAM-disrupting silent mutation, is shown. (b) Installation (via 4-bp insertion) and correction (via 4-bp deletion) of the pathogenic HEXA 1278+TATC allele in HEK293T cells. Correction either to wild-type HEXA, or to HEXA containing a PAM-disrupting silent mutation, is shown. (c) Installation of the protective G127V variant in PRNP in HEK293T cells via G•C-to-T•A transversion. (d) Installation of a G•C-to-T•A transversion in DNMT1 of mouse primary cortical neurons using a split-intein PE3 lentivirus system (see Methods). Sorted values reflect editing or indels from GFP-positive nuclei, while unsorted values are from all nuclei. (e) PE3 editing and indels or (f) Cas9-initiated HDR editing and indels at endogenous genomic loci in HEK293T, K562, U2OS, and HeLa cells. (g) Targeted insertion of a His6 tag (18 bp), FLAG epitope tag (24 bp), or extended LoxP site (44 bp) in HEK293T cells by PE3. Editing efficiencies reflect sequencing reads that contain the intended edit and do not contain indels among all treated cells, with no sorting, except where specified in (e). Values and error bars reflect mean±s.d. of n=3 independent biological replicates.