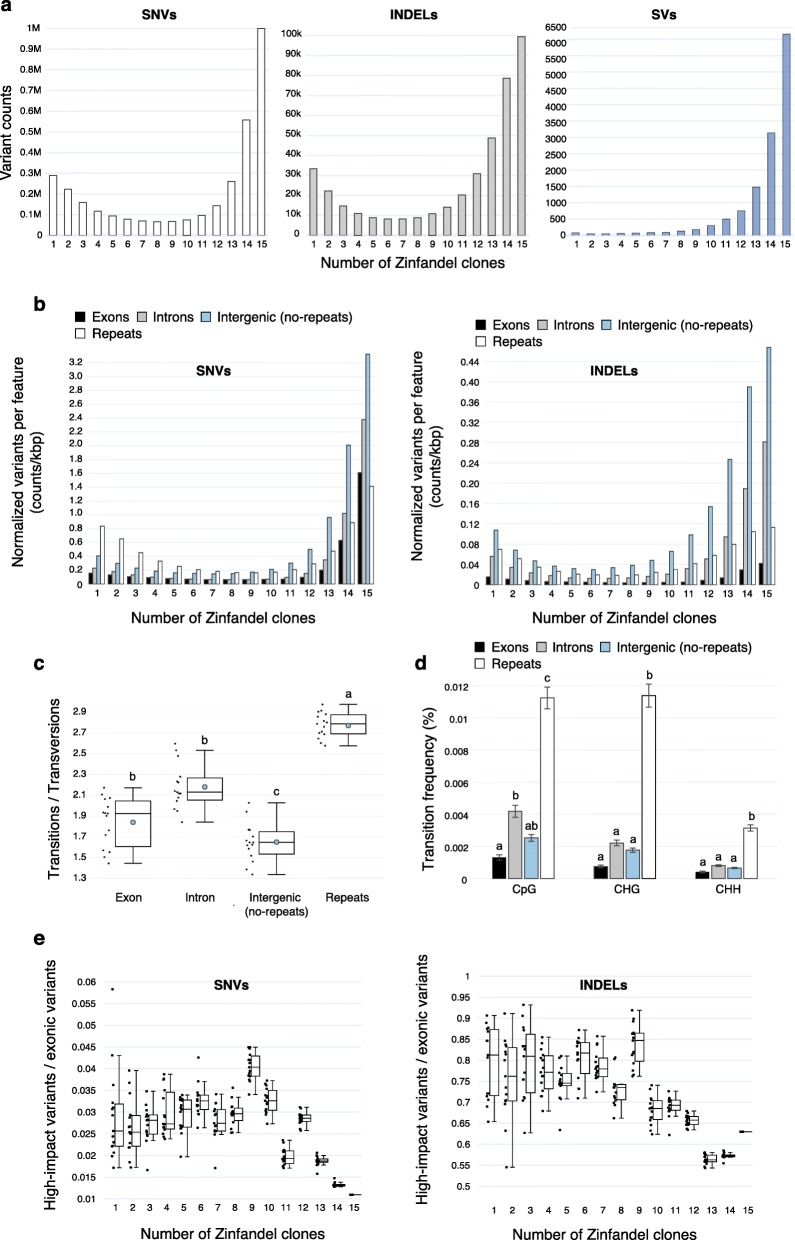
Fig. 5.
The abundance and impact of shared and unique heterozygous mutations among Zinfandel clones. Only loci at which all clones were called by GATK were used. a. The number of heterozygous SNVs, INDELs, and SVs shared by only N Zinfandel clone(s); b. The number of SNVs and INDELs shared by only N clone(s) in exons, introns, intergenic repeats (“Repeats”), and non-repetitive intergenic space; c. The ratio of transitions (Tr) to transversions (Tv) for heterozygous SNVs that uniquely occur in single Zinfandel clones and in different genome features. Different letters indicate significant differences in Tr/Tv rates between features (Tukey HSD, p < 0.01). The mean is shown as a blue circle; d. The mean percentages of CpG, CHG, and CHH in exons, introns, intergenic repeats (“Repeats”), and non-repetitive intergenic space that experience transition mutations. Standard error is shown. Heterozygous SNVs that uniquely occur in a single Zinfandel clone were used. Different letters indicate significant differences (Tukey HSD, p < 0.01); e. Proportion of exonic SNVs and INDELs that are putatively deleterious and shared by only N Zinfandel clone(s)