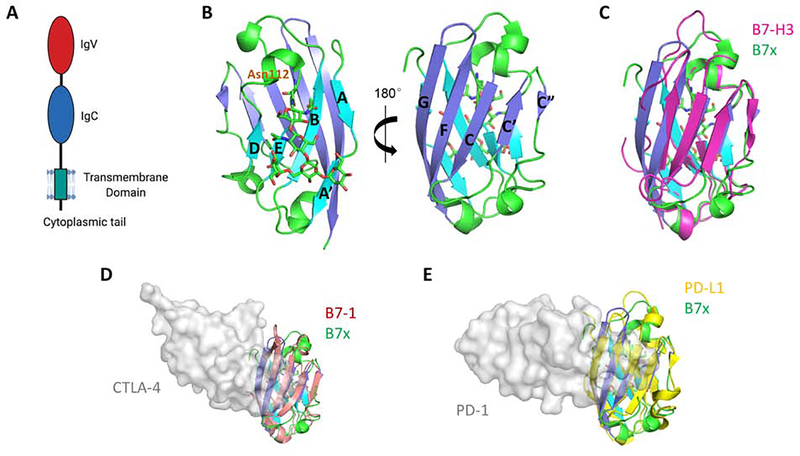
Figure 1. Structure of the Human B7x Protein and Its Comparison with Other B7 Ligands.
(A) Full length human B7x consists of the receptor-binding IgV domain, an IgC domain, a stalk region, a transmembrane domain, and a very short cytoplasmic tail with no signaling motif. (B) The crystal structure of the human B7x IgV domain is shown. The back-sheet, front-sheet and the connecting loops (PDB: 4GOS) are colored as cyan, blue and green respectively. Residue Asn112 and the linked glycan are shown as sticks. (C) Superimposition of human B7x with the reconstituted monomeric mouse B7-H3 model (colored as magenta) built from dimeric B7-H3 (PDB: 4I0K). (D) Superimposition of the IgV domain of human B7x with human B7–1 (colored as salmon). The receptor CTLA-4 is shown as grey surface to indicate the binding interface on B7–1 (PDB: 1I8L). (E) Superimposition of the IgV domain of human B7x with human PD-L1 (colored as yellow). The receptor PD-1 is shown as grey surface to indicate the binding interface on PD-L1 (PDB: 4ZQK), suggesting a possible interaction between B7x and its yet-unidentified receptor.