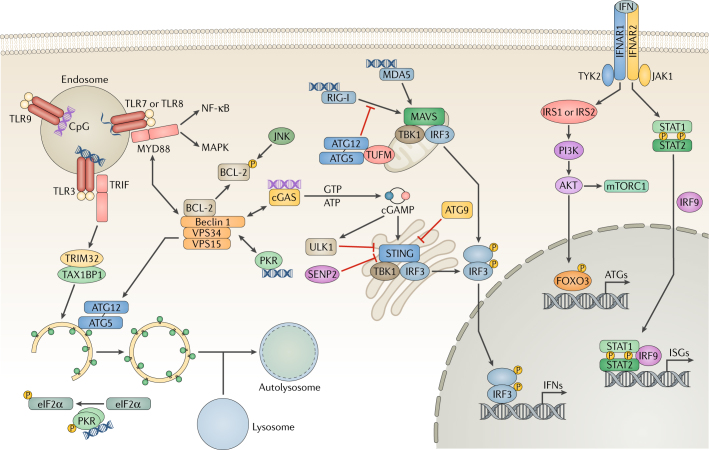
Fig. 1. Pattern recognition receptors and autophagy.
In host cells, various pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which leads to the activation of transcription factors and the induction of the interferon (IFN) response. Endosomal Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize viral nucleic acids and recruit the adaptor proteins TIR domain-containing adaptor molecule 1 (TRIF) and myeloid differentiation primary response protein MYD88, relaying signals to the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-associated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. Binding to MYD88 or TRIF causes Beclin 1 to dissociate from the B cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) inhibitory complex, resulting in the induction of autophagy. TRIF is targeted by selective autophagy by the tripartite motif-containing protein 32 (TRIM32)–TAX1-binding protein 1 (TAX1BP1) complex for degradation. JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylates BCL-2 to initiate Beclin 1-mediated autophagy. During RNA virus infection, retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) senses double-stranded (ds)RNA and signals through mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein (MAVS) to activate interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), leading to the production of IFN. To suppress RIG-I signalling, the autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)–ATG12 complex disrupts the interaction between RIG-I and MAVS. Interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) phosphorylates eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1 (eIF2α) to induce autophagy. During DNA virus infection, the DNA sensor cyclic GMP–AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) produces the secondary messenger cGAMP, which activates stimulator of interferon genes protein (STING), IRF3 and IFN expression. Furthermore, cGAS competes with Rubicon for Beclin 1 binding, thus triggering autophagy. Beclin 1 also suppresses cGAMP production and activates ULK1 to phosphorylate STING for its degradation. ATG9 inhibits the aggregation of STING on Golgi apparatus-derived compartments to suppress the DNA sensing. STING undergoes desumoylation and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA)-mediated degradation. Finally, extracellular IFN is recognized by the interferon receptor (IFNAR) and activates JAK–STAT (Janus kinase–signal transducer and activator of transcription) signalling. JAK1 and non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 phosphorylate insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) and IRS2, leading to the activation of the PI3K–AKT–mTOR (phosphoinositide 3-kinase–AKT–mechanistic target of rapamycin) pathway and forkhead box 3 transcription factor (FOXO3) as well as the expression of autophagy-related genes. ISGs, interferon-stimulated genes; MDA5, interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1; SENP2, sentrin-specific protease 2; TBK1, tank-binding kinase 1; TUFM, elongation factor Tu, mitochondrial; VPS34, vacuolar protein sorting 34.