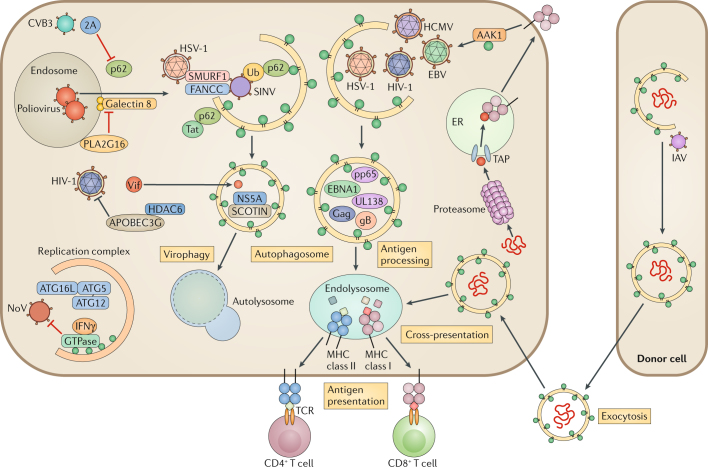
Fig. 2. Autophagy-mediated antiviral immune responses.
Autophagy targets intruding viruses by directly eliminating them in autophagosomes. Adaptor protein p62 binds to ubiquitin-coated viral particles that are subsequently delivered to the autophagic machinery. For example, p62 binds to Sindbis virus (SINV) capsid protein and mediates selective autophagy by interacting with LC3 through its LC3-interacting region (LIR). Two host factors, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF1 and Fanconi anaemia group C protein (FANCC), are involved in the virophagy of SINV and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). During hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, the host endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transmembrane protein SCOTIN associates with HCV non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) and leads to its degradation, restricting HCV replication. Poliovirus infection and membrane rupture are detected by galectin 8, targeting the virus to autophagosomes. Poliovirus uses HRAS-like suppressor 3 (PLA2G16) to escape from autophagic degradation. HIV-1 virion infectivity factor (Vif) is targeted by histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) for degradation. The autophagy protein 5 (ATG5)–ATG12–ATG16L1 complex is recruited in the replication complex and restricts norovirus (NoV) replication through interferon-γ (IFNγ)-inducible GTPases. In antigen-presenting cells (APCs), autophagy delivers intracellular and extracellular antigens to the endolysosome, where they are loaded onto major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules for presentation to CD4+ T cells. EBV nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) is the dominant CD4+ T cell antigen and is primarily processed in the autophagosome. HIV-1 Gag is also targeted by the autophagosome for processing. Autophagy regulates the internalization of MHC class I molecules from the cell membrane via AP2-associated kinase 1 (AAK1). UL138 from human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and gB from HSV-1 are presented on MHC class I molecules in an autophagy-dependent pathway, when antigen peptide transporter (TAP)-dependent presentation is blocked. Autophagy also promotes an alternative pathway of class I presentation called cross-presentation. It modulates trafficking and processing of phagocytosed antigens from the endosome to MHC I, and autophagy induces antigen packaging in donor cells for release to APCs. 2A, protease 2A; CVB3, coxsackievirus B3; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; IAV, influenza A virus; pp65, 65 kDa phosphoprotein; TCR, T cell receptor; Ub, ubiquitin.