Fig 7. Regulation of the GA pathway by amiRNA46 and StTCP23.
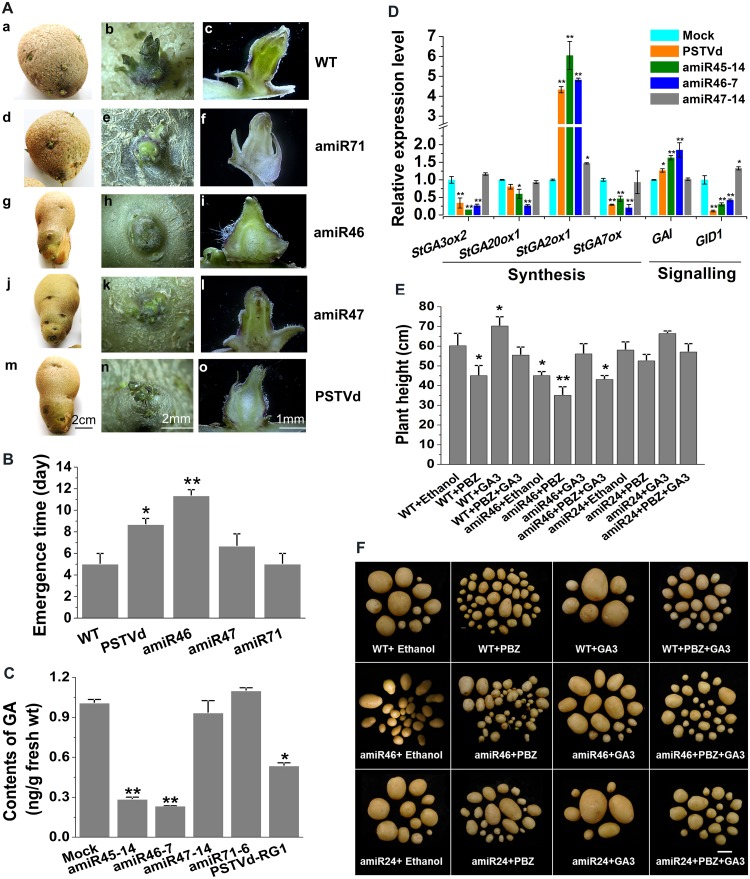
(A) Sprouting behavior of tuber discs prepared from amiRNA transgenic and control potato lines. (a, b, c), mock inoculated plants; (d, e, f), transgenic plants expressing amiR71; (g, h, i), transgenic plants expressing amiR46; (j, k, l), transgenic plants expressing amiR47; (m, n, o), PSTVd inoculated non-transgenic plants. (a, d, g, j, m), sprouting behavior of whole tubers, scale bar = 2 cm; (b, e, h, k, n), sprouting behavior of individual buds, scale bar = 2 mm; and (c, f, i, l, o), cross sections of individual sprouting buds under the scanning electron microscope, scale bar = 1 mm. (B) Delayed emergence of new stems in transgenic plants expressing amiR46, amiR47 and PSTVd-inoculated non-transgenic plants as compared with transgenic plants expressing amiR71 and uninoculated non- transgenic control plants. (C) Comparison of endogenous GA3 levels in uninfected control, amiR45, amiR46, amiR47, amiR71, and PSTVd-infected non- transgenic plants. (D) RT-qPCR quantitation of selected genes involved in gibberellin metabolism. Total RNA was extracted from tuber harvested at bulking stage during potato tuber development. (E) Comparison of plant height for the different treatments. (F) Morphology of tubers collected from non-transgenic and amiR46, amiR24 transgenic plants after treatment with ethanol, PBZ, or GA3. Scale bars = 3 cm.