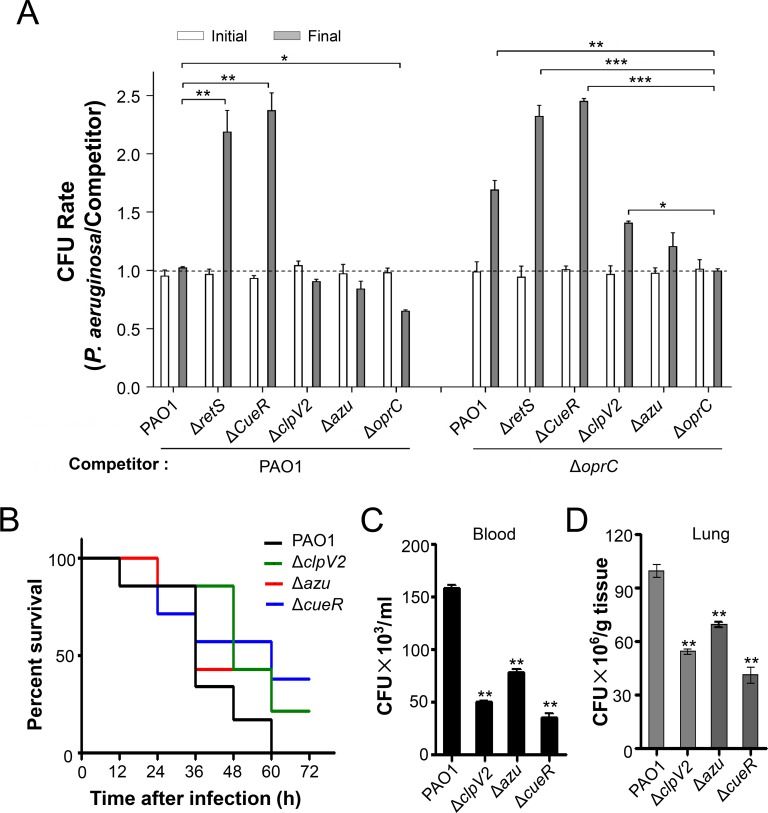
Fig 5. H2-T6SS-dependent Cu2+ transport system is important for competitive growth and virulence.
(A) OprC and Azu mediate H2-T6SS-dependent intrabacterial competition. The indicated strains were grown in LB medium supplemented with 0.25 mM EDTA for 6 h. Quantification of cfu before (initial) and after (final) growth competition assays between the indicated organisms. The cfu of the relevant P. aeruginosa versus competitor was plotted. Error bars represent the mean ± s.d. of three biological replicates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 based on two-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. (B) The clpV2, azu, and cueR deletion reduced the virulence of P. aeruginosa. C57BL6 mice were intranasally challenged with wild-type PAO1, ΔclpV2, Δazu, or ΔcueR at 1×107 cfu in 50 μl PBS, moribund mice were killed to obtain survival data (n = 6/strain). (C-D) Mice were infected with 1×107 wild-type PAO1, ΔclpV2, Δazu, or ΔcueR strain intranasally (n = 6/strain). At 12 h, serums and lungs from mice infected with no bacteria (PBS), or the indicated strains were recovered. Bacterial loads were determined by serial dilution and plating. **P<0.01 compared to wild-type PAO1 by Student's t test. The strains contain either the empty vector pAK1900 or the complemented plasmid.