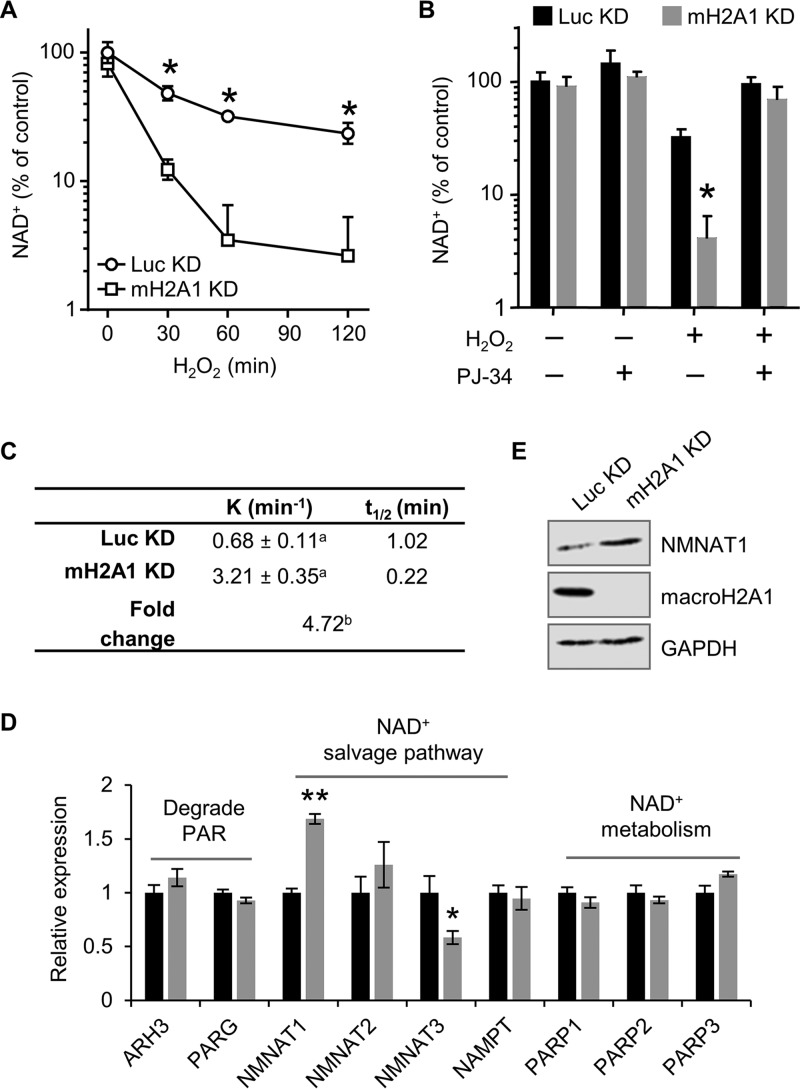
FIG 2.
MacroH2A1 prevents NAD+ depletion upon DNA damage. (A) Relative cellular NAD+ levels in IMR90 cells expressing shRNA against macroH2A1 (mH2A1 KD) or luciferase (Luc KD) as a control following 125 μM H2O2 treatment for the indicated times. (B) NAD+ levels relative to control for mH2A1 KD and Luc KD IMR90 cells treated for 2 h with 125 μM H2O2 and 10 μM PJ-34 where indicated. The bars and error bars represent the means and SEM of the results of at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; Student's t test. (C) Rate constant (K) and half-life (t1/2) of NAD+ in response to 125 μM H2O2 in control (Luc KD) and macroH2A1-depleted (mH2A1 KD) cells. a, standard error of the rate constant; b, P < 0.0001 (F test). (D) Relative expression (RT-PCR) of enzymes involved in NAD+ synthesis and metabolism in Luc KD and mH2A1 KD cells for four biological replicates. The bars and error bars represent means ± SEM. *, P = 0.02; **, P = 0.0007; Student's t test. (E) Immunoblots of total cell lysates for NMNAT1, macroH2A1, and GAPDH from Luc KD and mH2A1 KD cells.