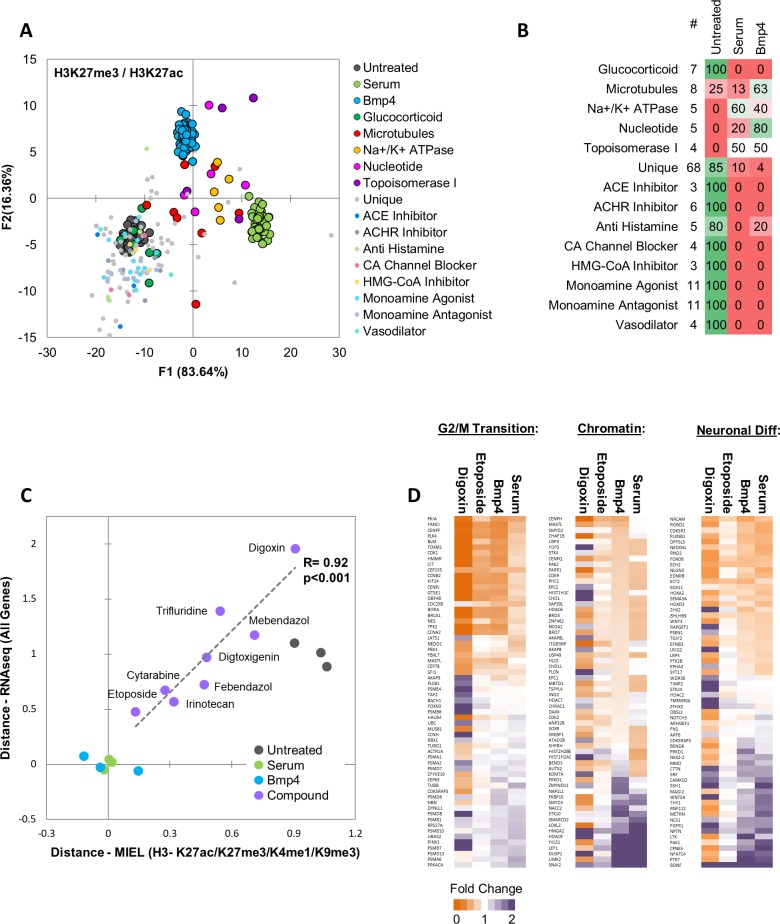
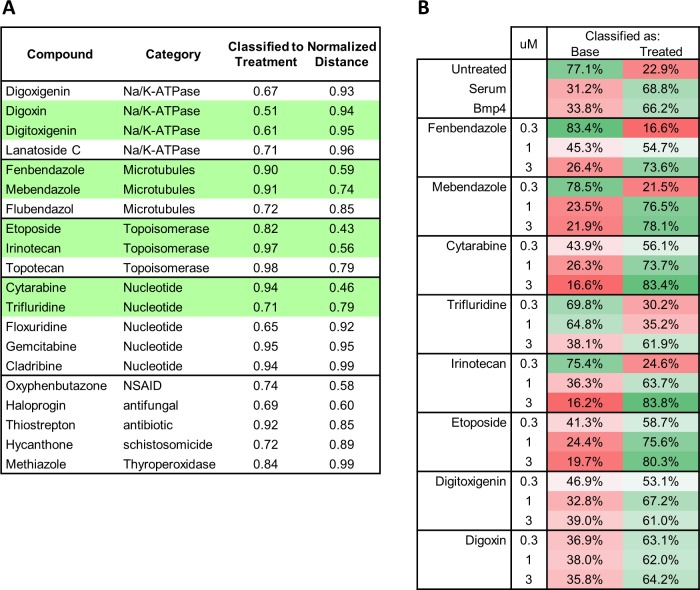
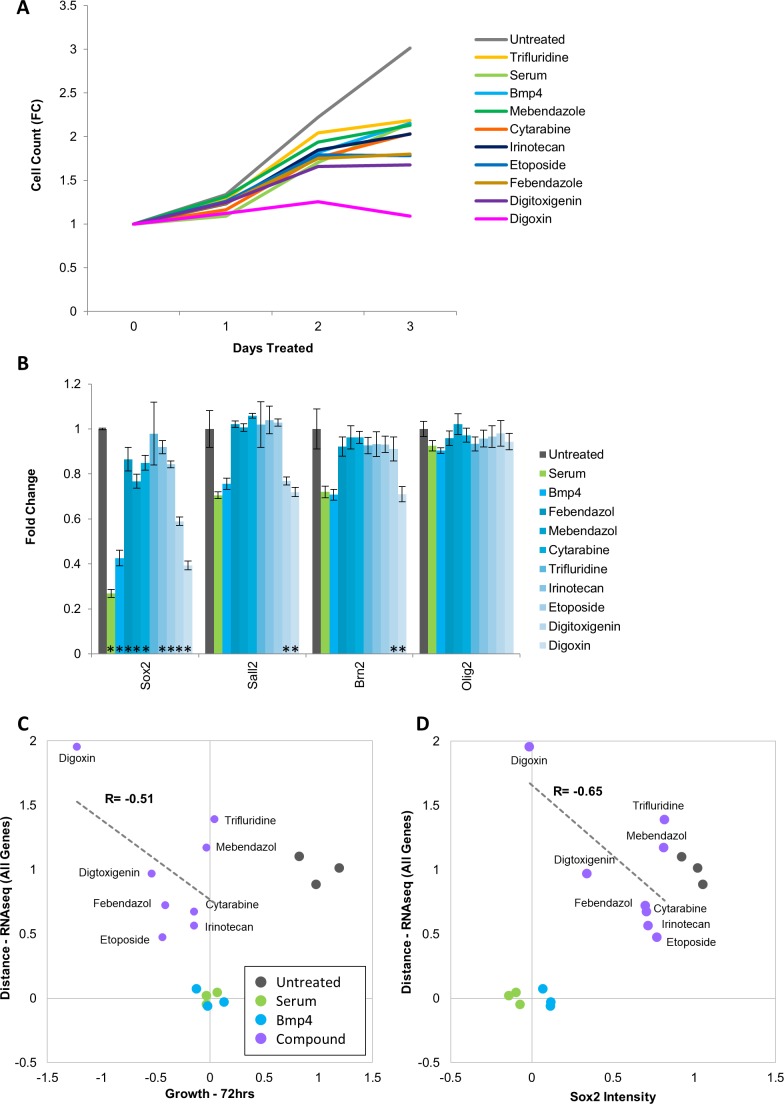
Figure 5. MIEL prioritizes small molecules based on serum/Bmp4 differentiation signature.
Quadratic discriminant analysis using texture features derived from images of untreated, serum-, Bmp4- and compound-treated GBM2 cells stained for H3K27me3, H3K27ac. Model was built to separate untreated, serum- and Bmp4-treated cells (60 technical replicates each). (A) Scatter plot depicting the first two discriminant factors for each population. (B) Confusion matrix showing classification of epigenetically active Prestwick compounds. Numbers depict the percent of compounds from each category classified as either untreated, serum or Bmp4 treated. (C) Scatter plot showing the correlation of gene expression profile-based ranking and MIEL-based ranking for eight candidate drugs, untreated, serum- or Bmp4-treated GBM2 cells. Euclidean distance to serum- or Bmp4-treated GBM2 cells was calculated using transcriptomic profiles (vertical axis) or texture features derived from images of H3K27ac and H3K27me3, H3K9me3, and H3K4me1 marks (horizontal axis). Distances were normalized to untreated and serum- or Bmp4-treated GBM2 cells. (D) Heat maps showing fold change in expression of select genes taken from the Gene Ontology (GO) list: cell cycle G2/M phase transition (GO:0044839), chromatin modification (GO:0006325), and regulation of neuron differentiation (GO:0045664). R denotes Pearson correlation coefficient. Drug concentrations a-c: febendazole = 0.5 µM, mebendazole = 0.5 µM, cytarabine = 0.3 µM, trifluridine = 3 µM, irinotecan = 0.5 µM, etoposide = 0.3 µM, digitoxigenin = 0.3 µM, digoxin = 0.3 µM.