Figure 1.
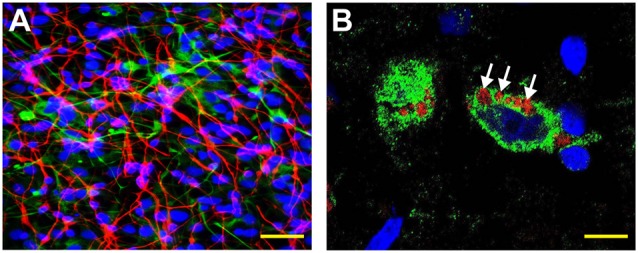
Human neuronal-glial (HNG) cells (transplantation grade) in primary co-culture were used to study the dynamics of amyloid-beta 42 (Aβ42) peptide-mediated entry of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) into neurons (Bhattacharjee and Lukiw, 2013; Zhan et al., 2018; Zhao and Lukiw, 2018a,b; Zhao et al., 2019). (A) HNG cells are a primary co-culture of neuronal [β-tubulin III (βTUBIII)-stained; red; λmax = 690 nm] and glial (GFAP-stained; green; λmax = 520 nm) human brain cells; HNG cells are also stained for nuclei (DAPI-stained; blue; λmax = 470 nm); cells shown are ~2 weeks in culture; HNG cells are about ~60% neurons (red) and about ~40% astroglial (green) at ~65% confluence; human primary neuronal and glial “support” cell co-cultures are utilized, because human neuronal cells do not culture well by themselves (Cui et al., 2010; Zhao et al., 2017c); HNG cells were exposed to 50 nM LPS for 36 h in the presence or absence of 10 nM Aβ42 peptides; other LPS concentrations at similar times displayed analogous trends; yellow scale bar (lower right) ~50 μm. (B) Affinity of LPS for the neuronal nuclear envelope (white arrows); LPS (red; λmax = 690 nm); β-tubulin III (βTUBIII)-stained (green; λmax = 520 nm) and nuclei (blue; λmax = 470 nm) stained HNG cells; white arrows indicate punctate and perinuclear clustering of LPS and LPS affinity for the nuclear envelope as has been previously reported (Hill and Lukiw, 2015; Zhan et al., 2016, 2018; Yang and Chiu, 2017; Zhao et al., 2017a,b); yellow scale bar (lower right) = 20 μm.
