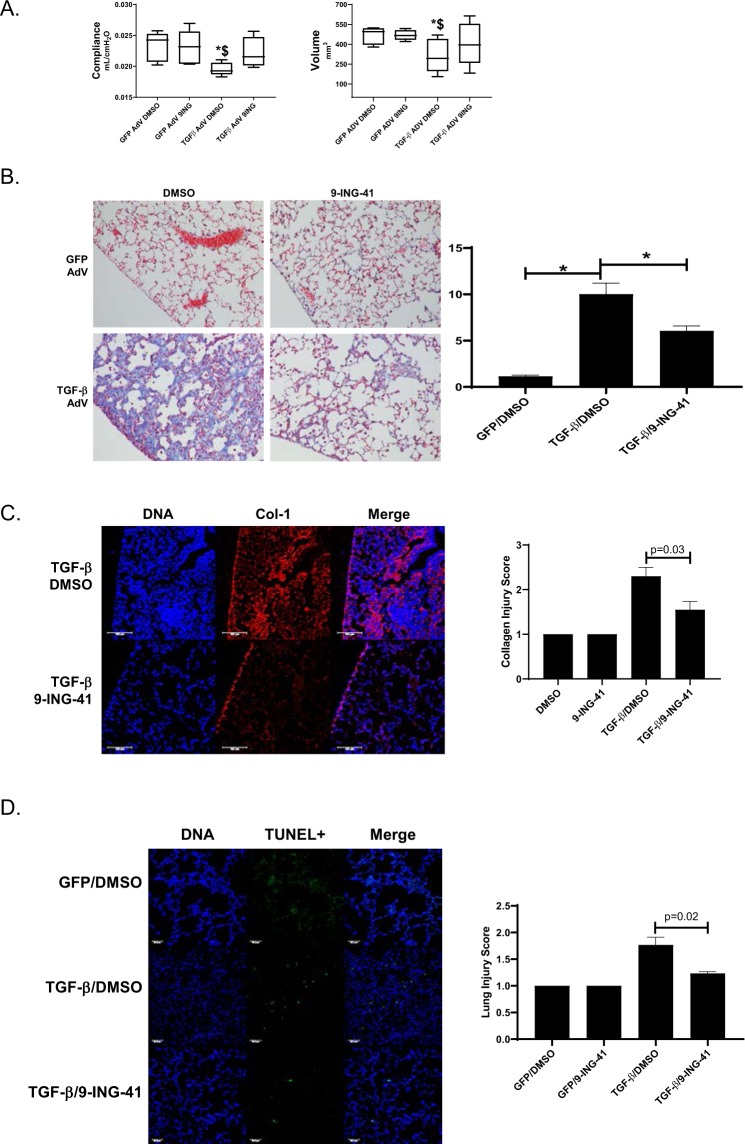
Figure 6.
9-ING-41-treated mice demonstrate reduced TGF-β mediated PF. Mice were intratracheally administered TGF-β adenovirus to induce pulmonary fibrosis. After 7d, mice received daily intraperitoneal injections of 9-ING-41 (30 mg/kg) for the next 7d. At the completion of the 14d time course, lung compliance and volumes were determined. A, Significant decrements in lung compliance and volume were reversed by 9-ING-41 treatment. Data are expressed as a mean ± SEM. n = 6 mice/condition. *Indicates a p < 0.05 compared to GFP adenovirus DMSO treatment. $Denotes p < 0.05 compared to GFP adenovirus 9-ING-41 treatment. B. Lung tissue sections from DMSO and 9-ING-41 treated mice were Trichrome stained to show areas of injury and collagen (blue). Images were taken at 20X optical zoom. Images are representative of 30 fields/slide/condition. n = 6–7 mice. Lung injury score data are expressed as means ± SEM. (C) Lung tissue sections from TGF-β adenoviral mice treated with vehicle and 9-ING-41 mice were immunostained to visualize collagen (Col-1) deposition (red) and nuclei (blue) by confocal microscopy. Images were taken at 25x optical zoom. Collagen injury score data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 6 mice/condition. Bar indicates 100 µm. (D) Lung tissue sections from GFP and TGF-β adenovirus infected mice were stained for apoptosis by fluorescent TUNEL stain (green) and nuclei (blue). Images were taken at 20X optical zoom. Images are representative of 15 fields/slide/condition and n = 5–6 samples/condition. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. p denotes a p < 0.05. Bar indicates 50 µm.