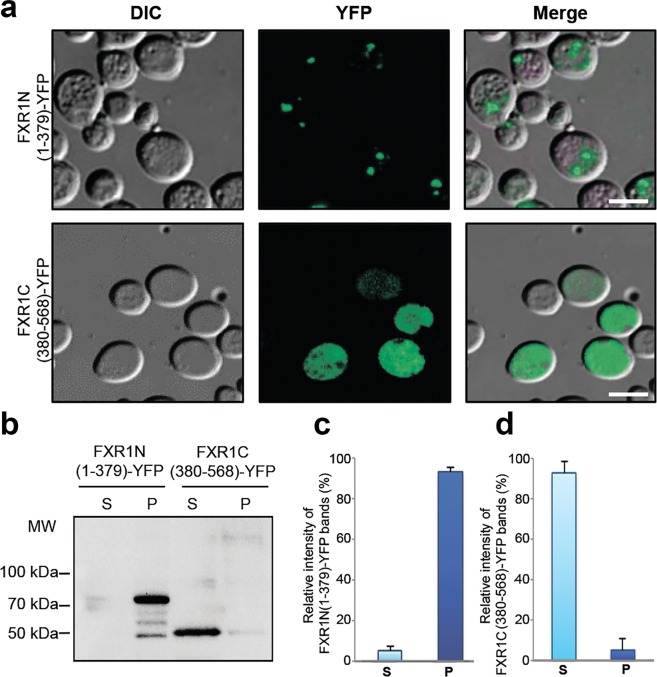
Figure 4.
Amyloid aggregation of FXR1 protein depends on its N-terminal region. (a) The FXR1N(1-379)-YFP protein forms visible aggregates in yeast cells, whereas FXR1C(380-568)-YFP is evenly distributed in cytoplasm. Scale bar, 10 µm. Three independently obtained transformants expressing the FXR1N(1-379)-YFP and FXR1C(380-568)-YFP proteins were included in the analysis. About one hundred cells of each transformant were analyzed. (b) Protein lysates expressing the FXR1N(1-379)-YFP and FXR1C(380-568)-YFP proteins were centrifuged, separated into the soluble and insoluble fractions and analyzed by immunoblotting. The FXR1N(1-379)-YFP protein forms insoluble aggregates, whereas the FXR1C(380-568)-YFP is present in soluble form. P – pellet fraction; S - supernatant fraction. (c,d) - Relative intensities of bands corresponding to monomers and aggregates of FXR1N(1-379)-YFP and FXR1C(380-568)-YFP represented as mean ± SEM, for three independent protein samples.