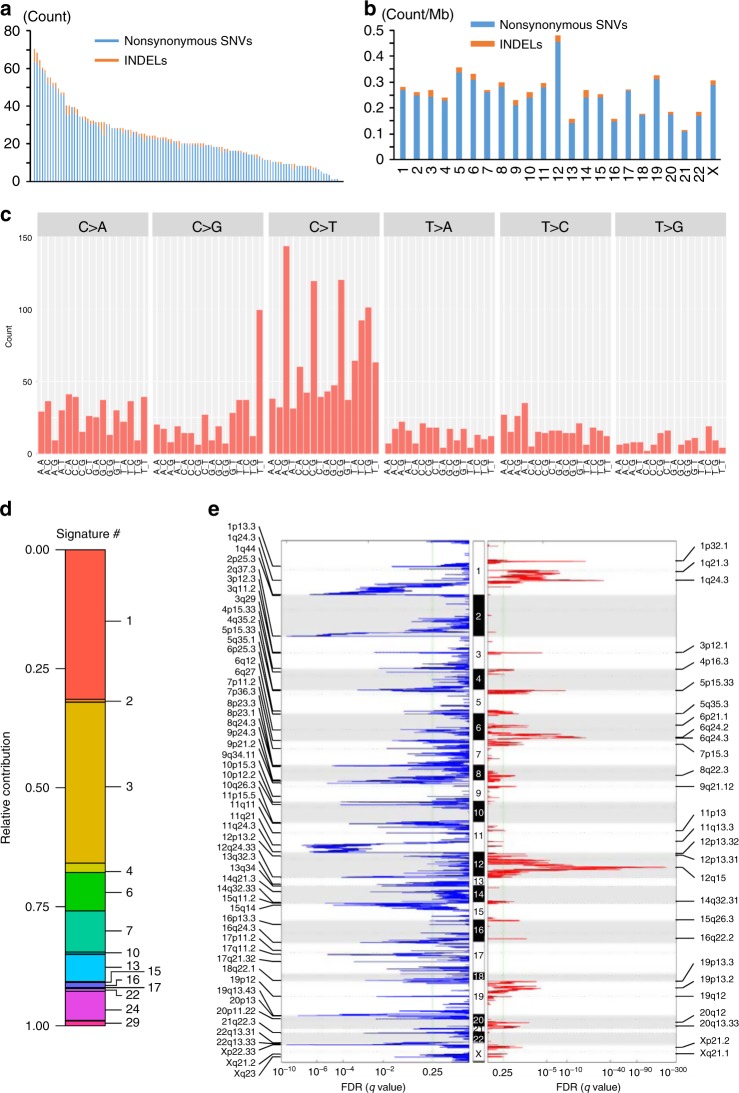
Fig. 1.
Characteristics of the somatic mutations and copy-number alterations in DDLPS. a Frequency of nonsynonymous SNVs and short INDELs identified by exome sequencing for each DDLPS sample. b Mean mutation frequency per megabase of coding sequence for each autosomal chromosome. Light blue and orange bars represent the frequency of SNVs and short INDELs, respectively. c 96 substitution classification for DDLPS samples. SNVs were classified according to six base substitution patterns, C > A, C > G, C > T, T > A, T > C, and T > G, and also based on the identity of the bases immediately 5′ and 3′ to each mutated base. d Mutation signature analysis for 119 DDLPS samples. The values represent the contribution of each signature (left) and the signature number (right). e Chromosomal regions with gained (red) and lost (blue) SCNAs identified in 119 DDLPS samples using GISTIC 2.0. The genes in each region are listed in Supplementary Data 1 and 2.