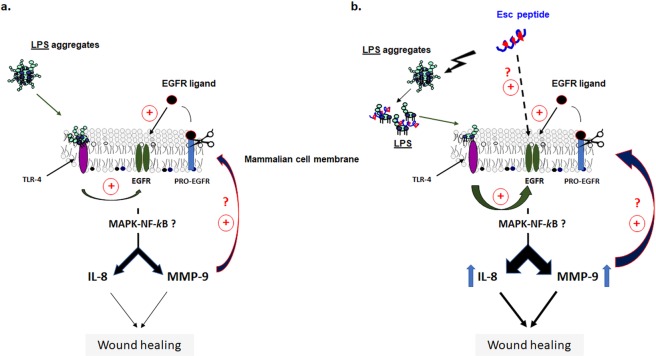
Figure 8.
Panel a: Schematic representation of the wound healing activity in airway epithelium by LPS-mediated activation of EGFR to simulate an infection condition. Activation of EGFR leads to IL-8 and MMP-9 production (likely through MAPK signaling pathway) which are involved in the wound healing process. MMP-9 would also contribute to cleave EGFR-proligands, thus leading to transactivation of EGFR. Panel b: The same representation showing the plausible mechanism of enhanced wound healing process after Esc peptides treatment. By disrupting LPS aggregates into smaller size particles, Esc peptides would allow LPS monomers to activate EGFR, via LPS-TLR4-mediated pathway. In addition, peptides treatment provokes an increased expression of IL-8 and MMP-9.