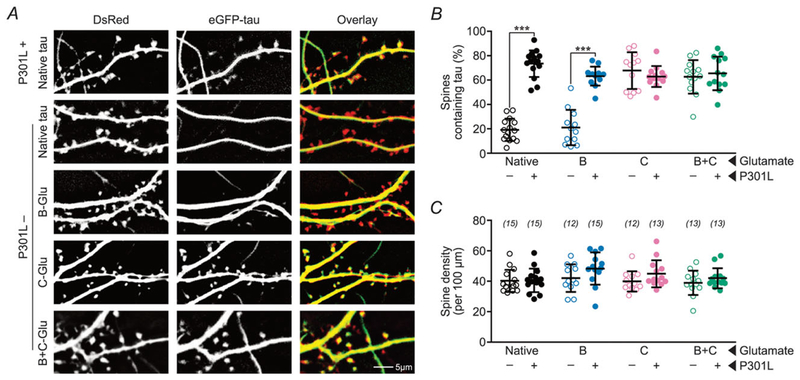
Figure 2. Pseudophosphorylation of C-domain residues enhances the mislocalization of wild-type tau to dendritic spines.
A, representative photomicrographs of eGFP–tau constructs (green) and DsRed (red) expressed in rat primary hippocampal neuronal cultures. ‘-Glu’ indicates glutamate substitutions of S/T residues to mimic phosphorylation in the respective domains. The mislocalization of tau with pseudophosphorylated C-residues (4th row) is comparable to that of P301L mutant tau (1st row). The addition of B-Glu mutations to tau with C-Glu mutations does not further increase the mislocalization of tau (5th row). B, quantification of percentage of spines containing tau. C, quantification of total spine density. Data were analysed by two-way ANOVA shielded Bonferroni post hoc analysis. In B, F(3, 98) = 40.45; ***P < 0.0001. In C, F(3, 98) = 0.699. n (number of neurons) is represented in parentheses. Error bars represent mean ± SD.