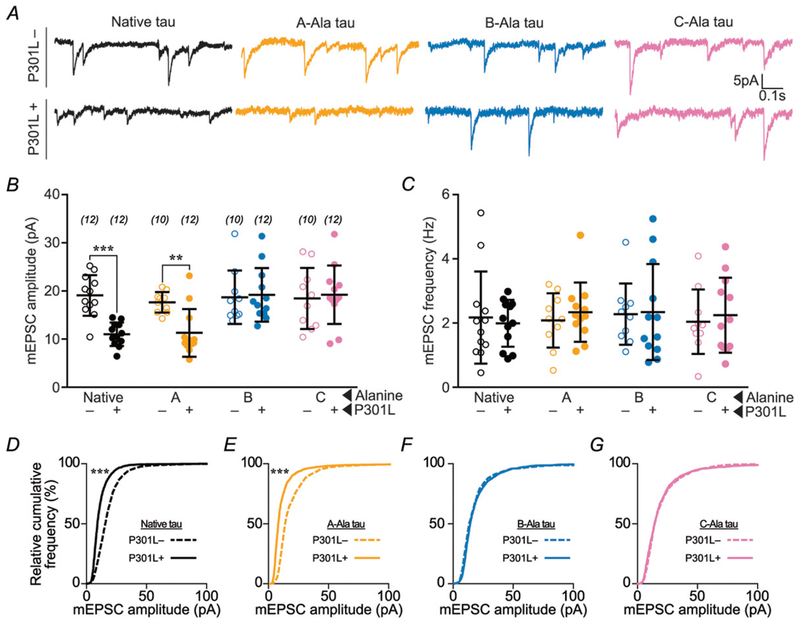
Figure 3. Blocking phosphorylation of B- or C-domain residues prevents P301L mutant tau-induced glutamatergic postsynaptic deficits.
A, representative traces of rat hippocampal neurons transfected with eGFP–tau constructs. Neurons were bathed in ACSF containing TTX (1 μM), picrotoxin (100 μM), and APV (100 μM) to isolate AMPA receptor mEPSCs. P301L mutant tau-containing constructs led to a reduction in mEPSC amplitude, except when either the B-residues or the C-residues were mutated to alanine to prevent phosphorylation. B, quantification of mEPSC amplitudes. C, quantification of mEPSC frequencies. D–G, relative cumulative frequency of amplitudes of all mEPSC events in multiple groups. In B and C, data were analysed by two-way ANOVA shielded Bonferroni post hoc analysis. In B, F(3, 79) = 5.082; native: ***P = 0.0005, A: *P = 0.0179. In C, F(3, 79) = 0.4394. In D–G, data were analysed by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov GOF test; ***P < 0.0001. Error bars represent mean ± SD. n (number of neurons) is represented in parentheses.