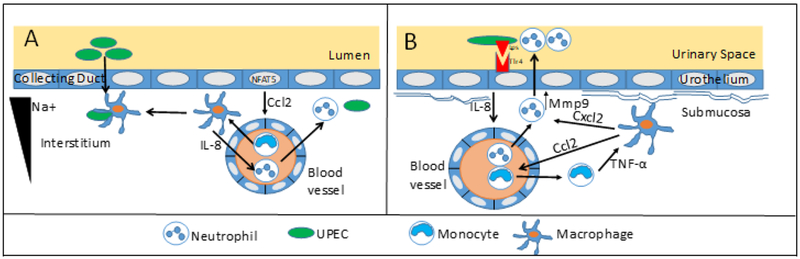
Figure 3.
Leukocyte-epithelial cell interactions orchestrate the innate immune response to UPEC (A) Tubular cells establish the medullary Na+ gradient and secrete the chemokine Ccl2 in a NFAT5 dependent manner. [57] Ccl2 recruits circulating monocytes, which differentiate into macrophages These macrophages increase phagocytosis, IL-8 dependent neutrophil recruitment, and antimicrobial activity in the presence of sodium. This network of myeloid cells serves a critical role in limiting interstitial spread of bacteria. (B) Urothelial cells express TLR4 that recognizes bacterial LPS, resulting in production of IL-8 that elicits neutrophil chemotaxis. Efficient neutrophil transepithelial migration relies on resident macrophages, which recruit circulating monocytes in a Ccl2-dependent manner. Monocyte TNF-α stimulates macrophages to secrete Cxcl2. Cxcl2 stimulates neutrophil production of Mmp9, which degrades matrix and promotes efficient transepithelial neutrophil migration to the urinary space.[37, 60]