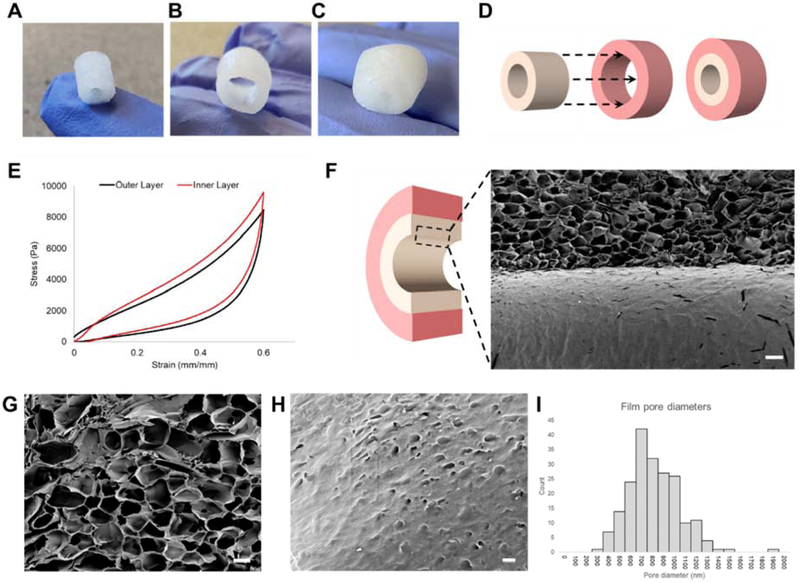
Figure 1. Dimensions, stiffness, and porous film characterization of lyophilized silk matrices.
3D scaffold systems for intestinal tissue engineering were fabricated used silk fibroin. (A) Inner scaffolds are cylindrical constructs with an outer Ø of 6 mm, inner Ø of 2 mm, and length of 8 mm. (B) Outer scaffolds are wider cylindrical constructs capable of enclosing the inner scaffold with an outer Ø of 10 mm, inner Ø of 6 mm, and length of 8 mm. (C) Silk scaffold system with inner and outer scaffold combined (D) Dimensions of inner and outer scaffolds allow sliding of the inner scaffold into the hollow center of the outer scaffold. (E) Representative tress-strain curves of both outer and inner scaffolds (F) SEM cutaway of the interface between the film and sponge (scalebar: 200 μm) (G) Interconnected pores in the spongey bulk of scaffolds (scalebar: 100 μm) (H) Nanopores in the film (scalebar: 2 μm). (I) Aggregate diameters of nanopores (n=201) averaged at 767 nm (s.d. = 233 nm).