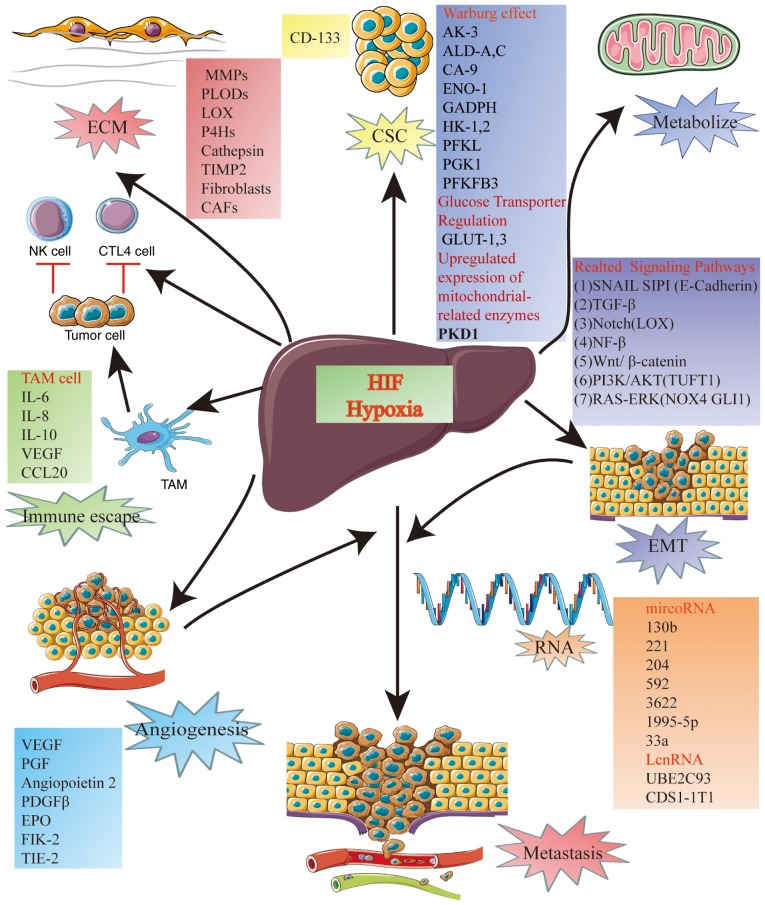
Figure 3.
Relationship between HIF and HCC. The complex relationship between HIF and HCC includes metabolism, immune escape, angiogenesis, metastasis, extracellular matrix remodeling, and cancer stem cells. ALD, aldolase; AK3, adenylate kinase 3; CA9, carbonic anhydrase 9; CCL20, CAFs, cancer-related fibroblasts; C-C motif chemokine ligand 20; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ENO1, enolase 1; EPO, erythropoietin; GLUT, glucose transporter; HK, hexokinase; LOX, lysyl oxidase; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NOX4, NADPH oxidase 4; P4Hs, prolyl-4-hydroxylases; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PFKFB, 3,6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 3; PFKL, liver-type phosphofructokinase; PGF, placental growth factor; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; PLODs, procollagen lysyl hydroxylases; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; TIE-2, tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2; TIMP2, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2; TUFT1, tuftelin1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.