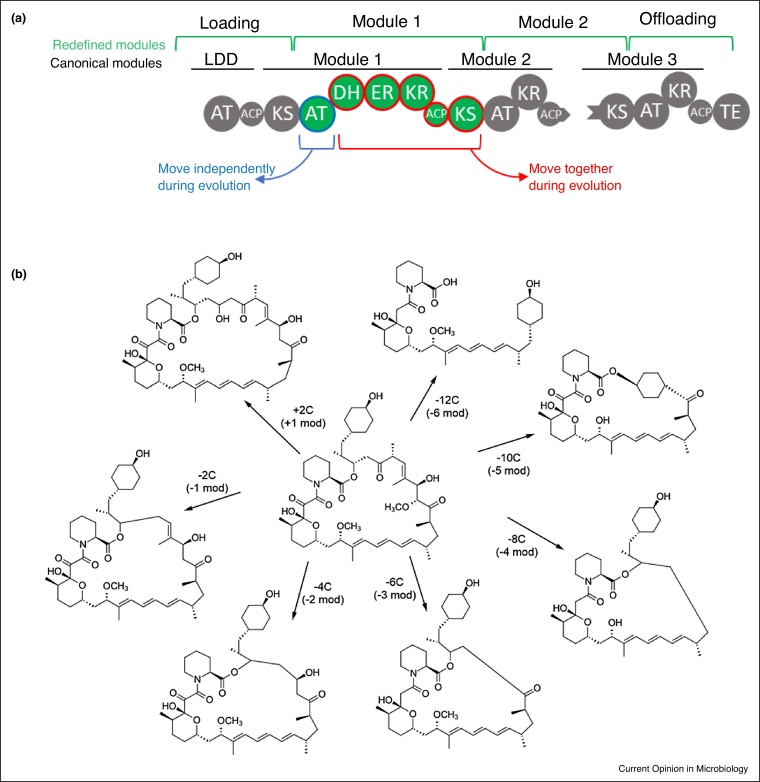
Figure 3.
Engineering polyketide synthases.
(a) Truncated representation of 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase. Like NRPS A-domains, the PKS acyltransferase (AT) domains select malonyl-derived coenzyme A (CoA)-linked extender units. The resulting malonate derivatives are transferred to acyl carrier proteins (ACP) which function like NRPS T-domains, and ketosynthase (KS) domains act like NRPS C-domains. PKSs also have additional tailoring domains present to modify the PK-chain, that is, ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH), enoylreductase (ER), and methyltransferase (MT) domains. The revised definition of modules (green) as well as co-evolving domains (blue, red) are highlighted. (b) Rapalogs, a diversity-oriented library of rapamycin derivatives gained by laboratory-scale evolution, termed ‘accelerated evolution’. Forced recombination events of the highly homologous rapamycin pathway lead to the loss of modules (mod) 1–6 or the addition of a second copy of module 13.