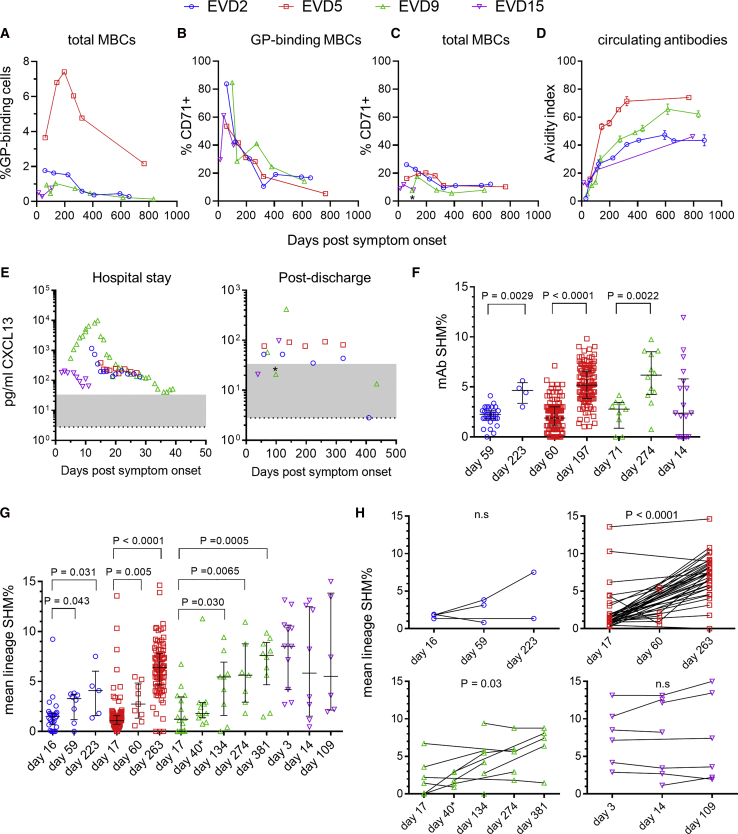
Figure 3.
Evidence for Prolonged B Cell Activation following EBOV Infection
(A) Frequency of GP-specific memory B cells over time. The percentage GPcl binding cells is shown.
(B and C) Prolonged activation of EBOV-specific MBCs. The percentage of cells expressing the activation marker CD71 is shown for GPcl binding MBCs (B) or total MBCs (C).
(D) Affinity maturation of GP-specific IgG. The avidity index is the percentage of GP-specific antibody (measured by ELISA) able to remain bound after washing with 8 M urea. The mean and standard deviation of three assays is shown.
(E) Longitudinal CXCL13 levels in serum. Plasma levels of the germinal center-associated chemokine CXCL13 were determined using a commercial assay. The normal reference range is shaded gray and the limit of detection is indicated by the dotted line. ∗Sample taken shortly after uveitis episode.
(F) Increase in SHM over time in GP-specific mAbs. Bars show the median SHM% and interquartile ranges. The p value for the Wilcoxon rank-sum test is shown.
(G and H) SHM% of GP-binding IGH lineages from repertoire sequencing. Unpaired analysis of all lineages that included sequences from GP-binding cells is shown in (G). Paired analysis of GP-binding lineages detectable at multiple time points is shown in (H). Bars show the median SHM% and interquartile ranges. p values are for the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (G) or the Wilcoxon signed-rank test (H). ∗EVD9 day 40 sequences were derived from sorted ASC RNA.