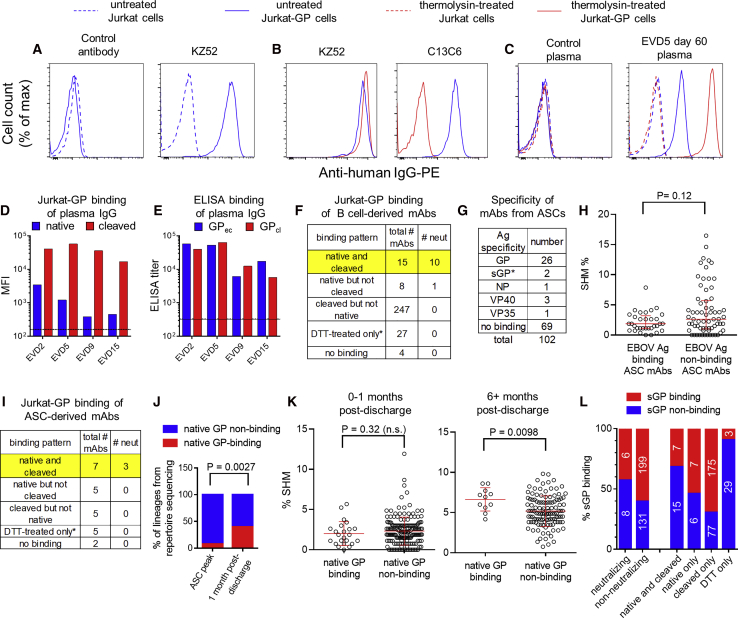
Figure 4.
Binding Properties of GP-Specific mAbs
(A–C) Cell surface binding assay. Histograms show the binding of mAbs (A and B) or plasma IgG (C) to Jurkat or Jurkat-GP cells. Thermolysin treatment was used to remove the glycan cap and mucin domains from GP. mAb KZ52 recognizes the GP base and mAb c13C6 recognizes the glycan cap.
(D) Binding of plasma IgG to native versus cleaved GP on cells. Untreated (native) or thermolysin-treated (cleaved) Jurkat-GP cells were stained with Ebola virus disease (EVD) patient plasma as in (C). The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is shown. Lines indicate the mean binding of IgG from three control donors to untreated cells (solid line) or thermolysin-treated cells (dashed line).
(E) Binding of plasma IgG to GPec versus GPcl by ELISA. Endpoint IgG ELISA titers are shown. Average titers for three control donors are shown for GPec (solid line) and GPcl (dashed line).
(F) Summary of B cell-derived mAb binding to cells. Binding was assessed on untreated (native) or thermolysin-treated (cleaved) Jurkat-GP cells. ∗mAbs that failed to bind to native or cleaved GP were tested for binding to Jurkat-GP cells treated with DTT.
(G) Specificity of mAbs from antibody secreting cells (ASCs). mAbs were cloned from EVD2 or EVD5 blood ASCs 1 month after discharge and their antigen specificities determined by ELISA. ∗mAbs were classified as sGP-specific if they bound sGP but not GPec, GPcl, or GPΔmuc.
(H) SHM levels in ASC-derived mAbs. The SHM% of mAbs that did or did not bind to an EBOV antigen are shown. Error bars indicate medians and interquartile ranges. The p value for the Wilcoxon rank-sum test is shown.
(I) Summary ASC-derived mAb binding to cells. As in (F).
(J) Increase in native GP-specific lineages 1 month after discharge. IGH lineages from the repertoire sequencing that included GP-specific mAbs were classified as native-GP binding if at least one of the included mAbs bound untreated Jurkat-GP cells. The p value shown is for Fisher’s exact test.
(K) Increased accumulation of SHM in native GP-binding mAbs over time. The p value for the Wilcoxon rank-sum test is shown.
(L) sGP binding of mAbs by category. mAbs were screened for sGP binding by ELISA and are classified according to their neutralization activity (left columns) or their Jurkat-GP binding phenotype (right columns).