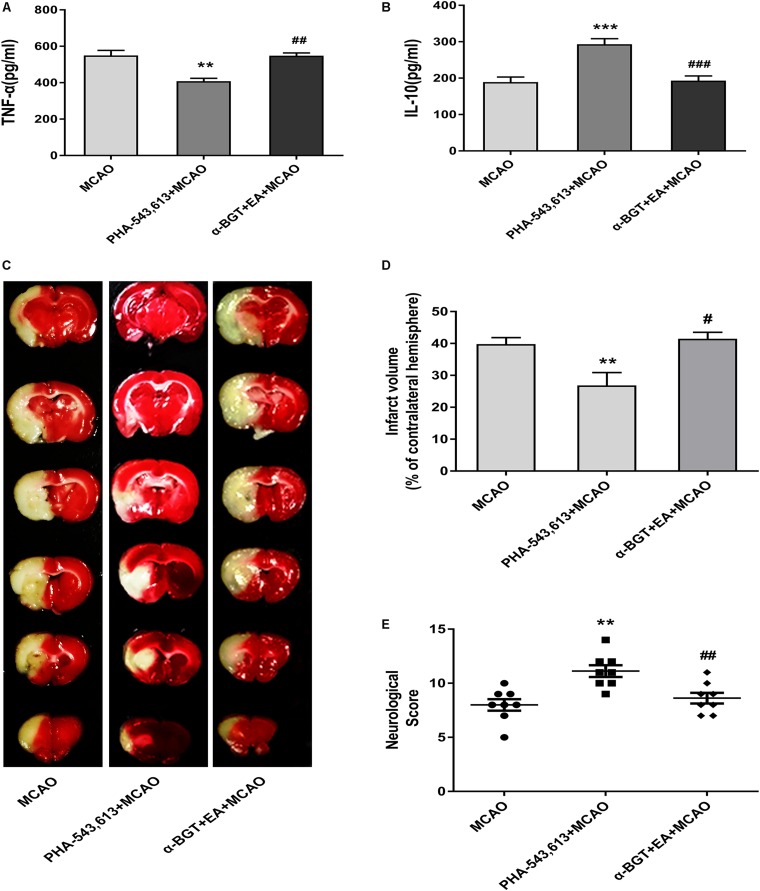
FIGURE 6.
EA pretreatment relieved inflammatory response and alleviated cerebral ischemia injury via α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR). (A,B) The level of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10) in the ischemic penumbra was detected 72 h after reperfusion by ELISA. The data were expressed as the mean ± SD and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. n = 5. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) group, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared with the PHA-543,613 + MCAO group. (C) Representative photographs of brain slices showing the infarct volume assessed 72 h after reperfusion. (D) The percentages of infarct volume. The data were expressed as the mean ± SD and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. n = 8. ∗∗p < 0.01 compared with the MCAO group, #p < 0.05 compared with the PHA-543,613 + MCAO group. (E) Neurological deficit scores were evaluated 72 h after reperfusion. The data were expressed as the median and were analyzed by the Mann–Whitney U-test. n = 8. ∗∗p < 0.01 compared with the MCAO group, ##p < 0.01 compared with the PHA-543,613 + MCAO group.