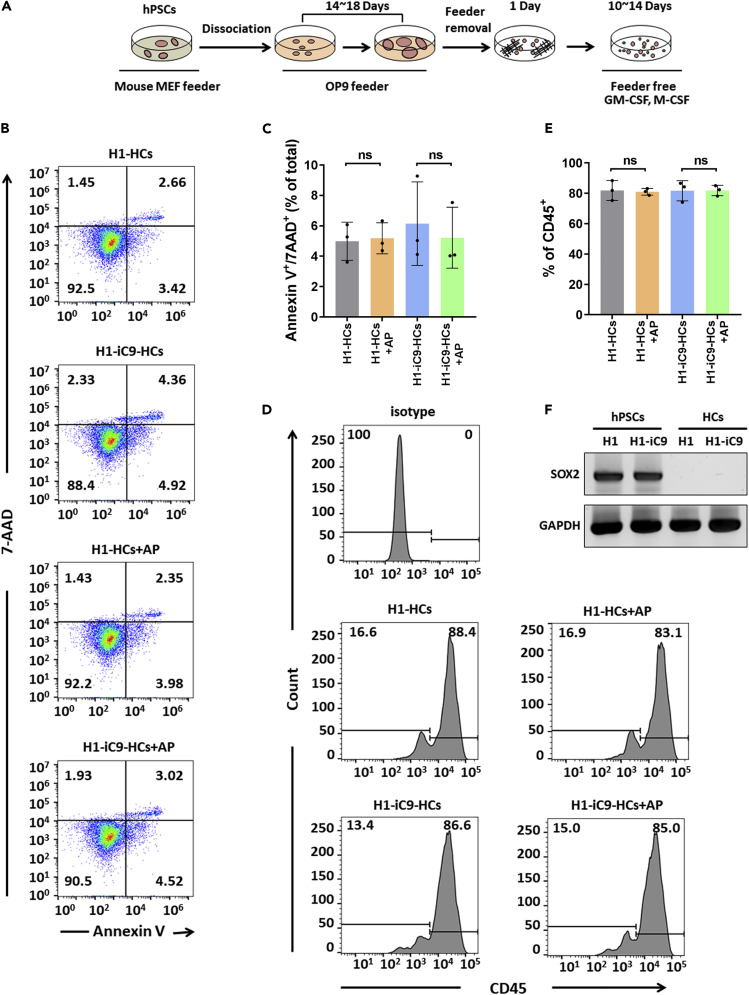
Figure 3.
Effect of AP1903 Treatment on H1-iC9-Derived Hematopoietic Cells
(A) Scheme of differentiation from hPSCs to hematopoietic cells.
(B and C) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis of hematopoietic cells derived from H1 and H1-iC9 cells with AP1903 treatment. Representative FACS profiles (B) and the bar graph showing percentage of apoptotic cells from three independent experiments (C) were shown and presented as the mean ± s.d. ns: p value not significant.
(D and E) The fraction of CD45+ hematopoietic cells derived from H1 and H1-iC9 differentiation was not affected by AP1903 treatment. Mock- or AP1903-treated hematopoietic cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. FACS plots (D) and bar graph that represents the frequency of CD45+ (E) were shown and presented as the mean ± s.d. (N = 3 independent experiments) ns: not statistically significant.
(F) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the SOX2 transcript in undifferentiated H1 and H1-iC9 cells as well as in the hematopoietic populations derived from these two cell lines.