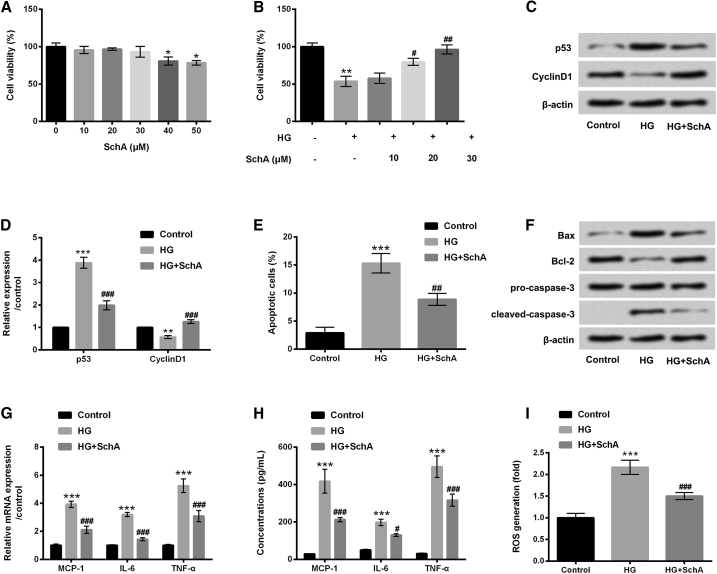
Figure 1.
SchA Alleviated HG-Induced ARPE-19 Cell Injury
(A) ARPE-19 cells were stimulated with SchA (10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 μM) for 24 h, and a CCK-8 assay was performed to determine the viability of ARPE-19 cells. (B) ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with SchA at the concentrations of 10, 20, and 30 μM and then exposed to high glucose for 48 h, after which a cell viability was assessed again using a CCK-8 assay. (C–I) ARPE-19 cells were pretreated with SchA (30 μM) and then received HG treatment for 48 h: (C) protein levels of p53 and CyclinD1 were examined by western blot assay, (D) quantitative analysis of p53 and CyclinD1 proteins, while (E) cell apoptosis, (F) apoptosis-associated proteins (Bax, Bcl-2, pro/cleaved-caspase-3), (G) relative mRNA expressions, (H) concentrations of MCP-1, IL-6, and TNF-α, and (I) ROS level were assessed by flow cytometry, western blot, quantitative real-time PCR, ELISA, and DCFH-DA staining. Data are shown as mean ± SD and were determined by three independent repeated experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus HG group.