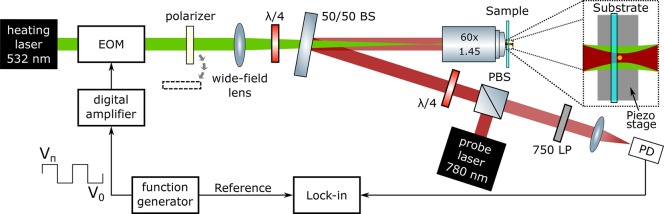
Figure 2.
Photothermal circular dichroism setup. Implementation of the PT CD microscope using a 532 nm wide-field heating beam and a tightly focused probe beam at 780 nm. The polarization modulation is achieved using an electro-optical modulator (EOM), leading to an alternatingly vertical and horizontal linear polarization state (the EOM acts as a zero and half-wave plate at 45° with respect to the incoming polarization). A quarter-wave plate (λ/4) transforms these states into LCP and RCP light. The removable polarizer is added to achieve intensity modulation, i.e., conventional photothermal imaging. The wide-field lens focuses the heating beam in the back-focal plane of the objective to obtain wide-field illumination of the sample. The probe beam from a Ti:sapphire laser is combined with the heating beam using a 50/50 beamsplitter tilted by a small angle (5°). To efficiently detect the backscattered light at the probe wavelength, a “cat-eye reflector” configuration was implemented.19 The detector is a fast photodiode with variable amplification. A long-pass filter (750LP) prevents direct detection of the heating beam. The generated signal is filtered by the lock-in amplifier set to the modulation frequency fm created in the function generator and amplified to feed the EOM.