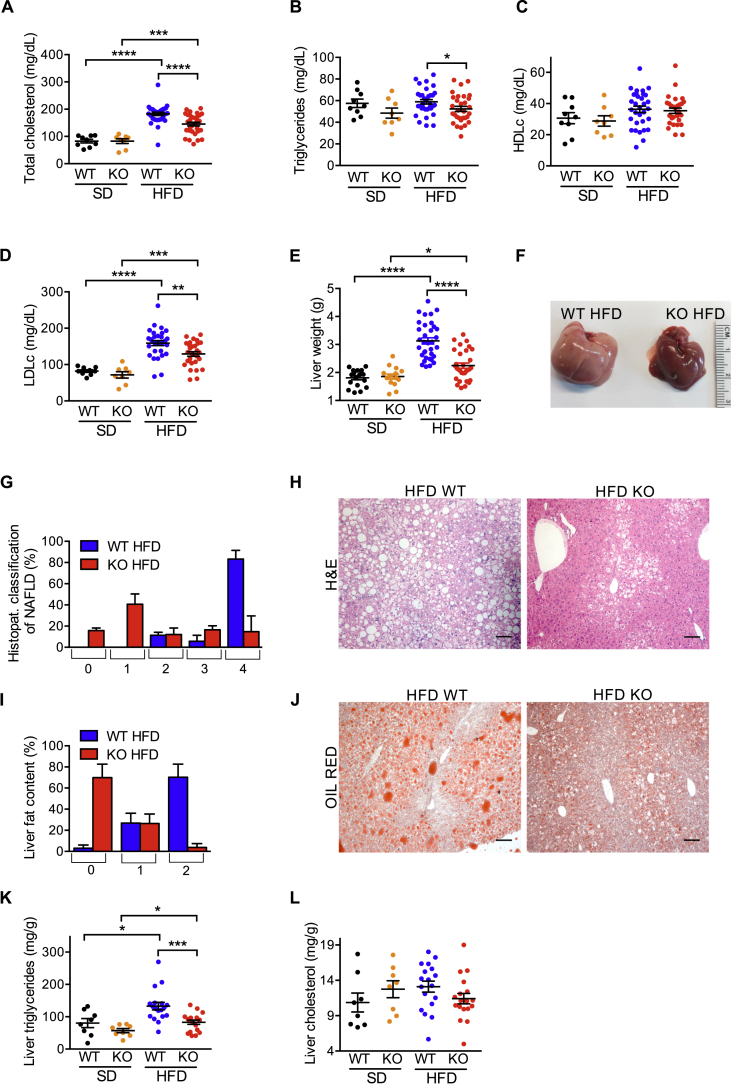
Figure 2.
iRhom2 KO mice are protected from dyslipidemia and NAFLD. A-D Colorimetric analysis of total cholesterol (A), triglycerides (B), HDL (C), LDL (D) in the serum of iRhom2 KO and WT mice fed with SD and HFD for 22 weeks. E Liver weight of iRhom2 KO and WT mice fed with SD and HFD for 30 weeks. Three independent HFD-induced obesity experiments, with 9–12 WT and 8–11 KO mice. The analysis of the SD-fed mice was performed on 2–3 groups of 3–7 mice per genotype. F–H Liver photographs (F), histopathological classification of NAFLD (scores ranging from no alterations (0) to a severe NAFLD phenotype (4) (G), and representative photographs of liver H-E staining (100x magnification) (H) of iRhom2 KO and WT mice described above fed with HFD for 30 weeks. I-J Liver fat content histopathological classification (scores ranging from within normal limits (0) to severe fat accumulation (2) (I), and representative photographs of liver Oil red staining (100x magnification) (J) of the mice described above fed with HFD. K-L Colorimetric analysis of liver triglycerides (K) and cholesterol (L) concentration in the animals described above fed with SD and HFD for 30 weeks. Two independent experiments with n = 6 or 12 HFD-fed mice and n = 2 or 6 SD-fed mice per genotype. Scale bar = 100 μm. Error bars represent SEM; * represents p < 0.05, ** represents p < 0.01, *** represents p < 0.001, **** represents p < 0.0001.