Fig. 2.
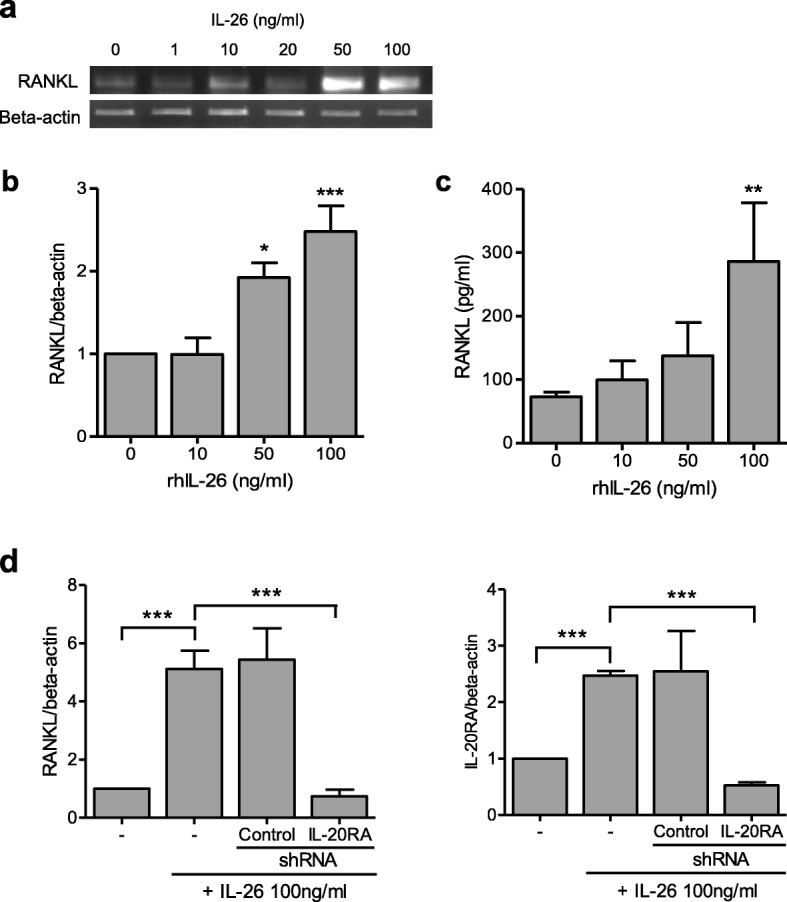
IL-26 induces RANKL expression in RA-FLSs. Following culture of RA-FLSs (n = 3) with 0–100 ng/mL of recombinant human (rh)IL-26 for 72 h, RANKL mRNA levels were determined by a reverse transcription PCR and b real-time PCR. Data were normalized to β-actin levels and presented as relative expression units. The image is representative of three experiments. c RA-FLSs were cultured with rhIL-26 for 72 h, and RANKL concentration in the culture media was measured by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. d RA-FLSs were cultured with 100 ng/mL of rhIL-26 and IL-20RA short-hairpin (sh) RNA or control shRNA for 72 h, and RANKL and IL-20 receptor subunit A mRNA levels were determined by real-time PCR. Target gene expression was normalized against β-actin expression. Data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005. IL interleukin, RANKL receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand, RA rheumatoid arthritis, FLSs fibroblast-like synoviocytes, PCR polymerase chain reaction
