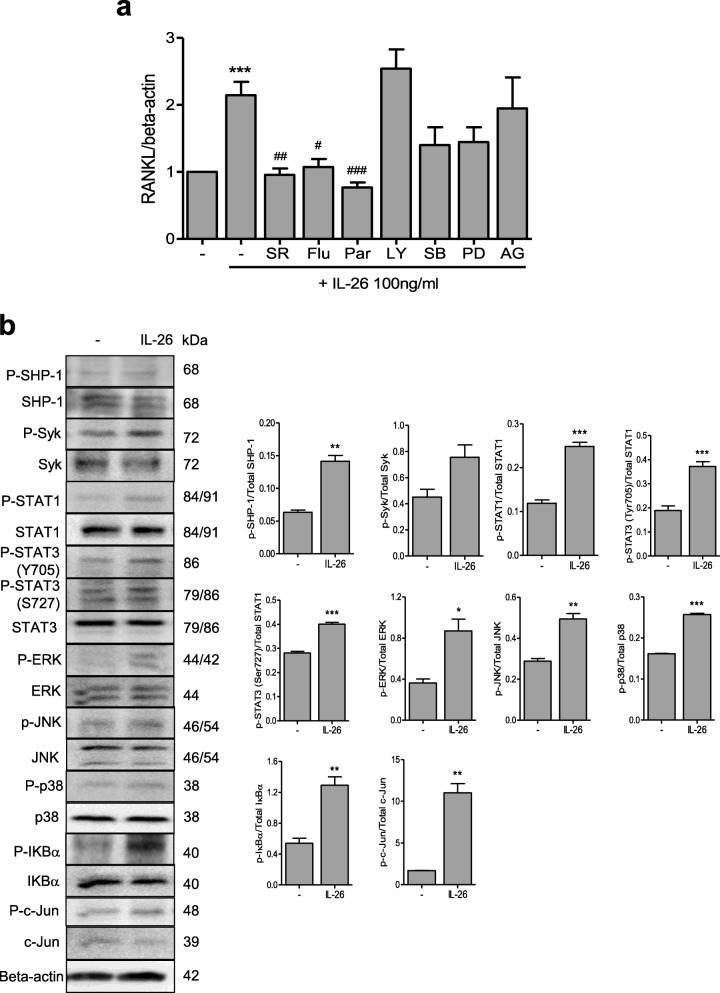
Fig. 3.
Downstream signaling pathways mediating IL-26-induced RANKL expression in RA-FLSs. a RA-FLSs (n = 3) were pretreated with SR11302 (AP-1 inhibitor) (1 μM), fludarabine (STAT1 inhibitor) (0.5 μM), parthenolide (NF-κB inhibitor) (10 μM), Ly294002 (PI3K inhibitor) (20 μM), SB203580 (MAPK inhibitor) (10 nM), PD98059 (ERK inhibitor) (20 μM), or AG490 (JAK2 inhibitor) (50 μM) for 1 h, followed by culture with 100 ng/mL of IL-26 for 72 h. RANKL mRNA level was quantified using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and normalized against β-actin expression. Data were expressed as relative RANKL/β-actin level. b RA-FLSs (n = 3) were cultured with 100 ng/mL IL-26, and phosphorylation of signaling-related molecules was assessed in cell lysates using western blot. Data were expressed relative to β-actin level and represent the mean ± standard error of the mean of three independent experiments. ***P < 0.005 vs. control; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.005 vs. IL-26. IL interleukin, RANKL receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand, RA rheumatoid arthritis, FLSs fibroblast-like synoviocytes