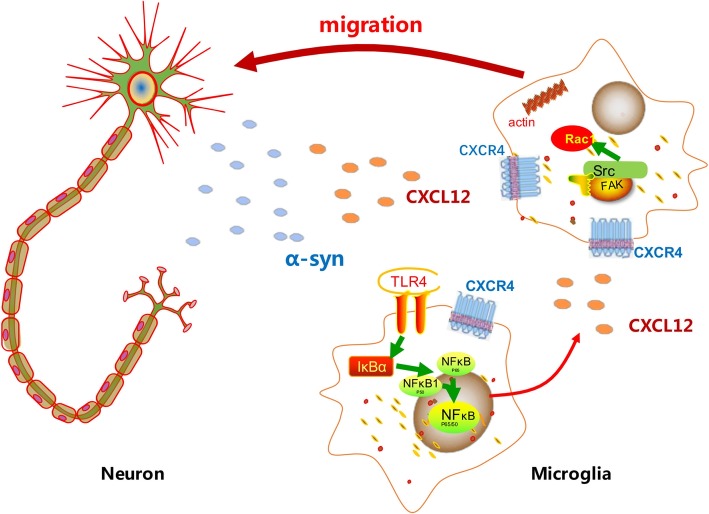
Fig. 6.
Schematic of the mechanism by which α-synuclein induces the accumulation of microglia through CXCL12/CXCR4. Released α-syn establishes a gradient in the space between the neurons and the microglia. α-Syn aggregates may bind to the TLR4 on microglia, eliciting an overexcretion of CXCL12 through TLR4/IκB-α/NF-κB signaling. CXCL12 participates in α-synuclein-induced microglial migration through binding to CXCR4 through the CXCL12/CXCR4/FAK/Src/Rac1 pathway. As a result, the microglia continue to migrate along the concentration gradient of α-syn and CXCL12 toward the sources of α-syn