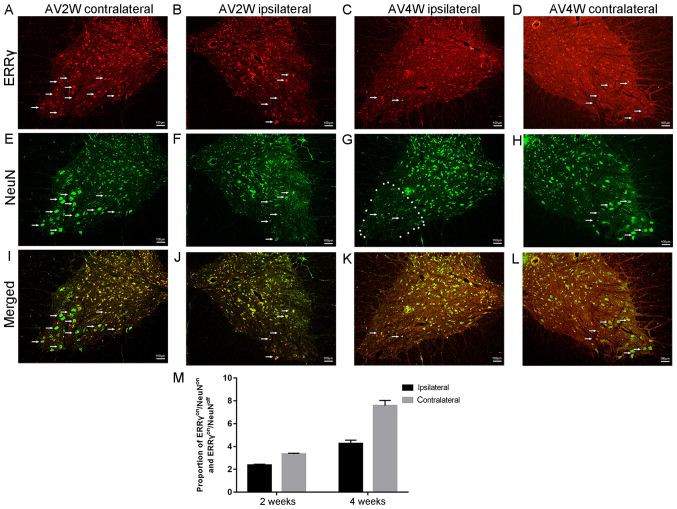
Figure 4.
Complementary expression of ERRγ and NeuN in γ and α motor neurons. Immunofluorescence double-labeling reaction results indicated that the positive immunoreactions at (A) 2 weeks in the contralateral side of the spine, (B) 2 weeks in the ipsilateral side of the spine, (C) 4 weeks in the ipsilateral side of the spine and (D) 4 weeks in the contralateral side of the spine. ERRγ (red) were located in the cytoplasm of the spinal neurons. The figures also show the apparent downregulation of the ERRγ signal on the injured ipsilateral sides at the time points after avulsion. NeuN (green) signals were concentrated in the nuclei of motor neurons as shown after (E) 2 weeks in the contralateral side of the spine, (F) 2 weeks in the ipsilateral side of the spine, (G) 4 weeks in the ipsilateral side of the spine and (H) 4 weeks in the contralateral side of the spine. Representative micrographs after (I) 2 weeks in the contralateral side of the spine, (J) 2 weeks in the ipsilateral side of the spine, (K) 4 weeks in the ipsilateral side of the spine and (L) 4 weeks in the contralateral side of the spine show that the bulk all of the ERR γ-positive motor neurons were also NeuN-positive motor cells (ERRγon/NeuNon). However, the remainder of these ventral motor neurons were ERRγon/NeuNoff. (M) ERRγ was detected in both populations of motor neurons ERRγon/NeuNoff status of motor neurons can be identified as γ motor neurons. ERRγ, estrogen-related receptor γ; NeuN, RNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 3.