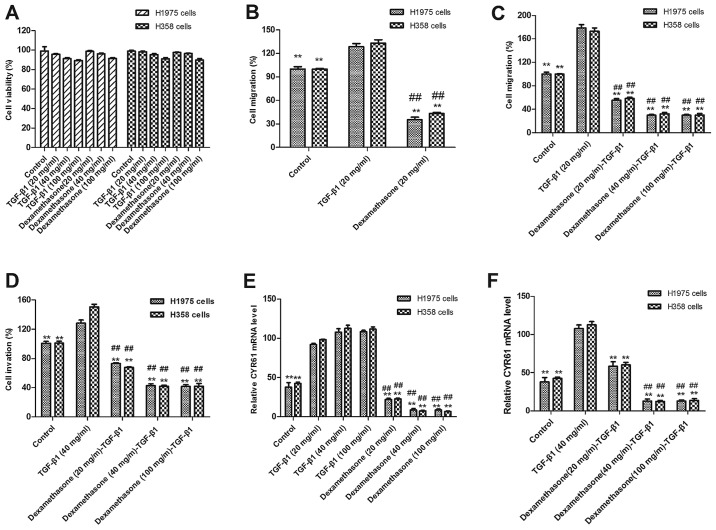
Figure 1.
Effects of dexamethasone on TGF-β1-induced migration and invasion in NSCLC. (A) Cell viabilities did not change in dexamethasone-treated and TGF-β1-treated H1975 and H358 cells at different doses compared with the control. (B) TGF-β1 promoted and dexamethasone inhibited migration of NSCLC H1975 and H358 cells following 12-h exposure compared with control cells. (C) Dexamethasone treatment eliminated the effect of TGF-β1-induced promotion of migration at 20, 40 and 100 mg/ml following 12-h exposure, as compared with untreated and TGF-β1-treated cells. (D) TGF-β1 promoted and dexamethasone inhibited the invasion of NSCLC H1975 and H358 cells at dose of 40 mg/ml following 12-h exposure compared with control cells. (E) Dexamethasone treatment eliminated the effect of TGF-β1-induced promoted invasion at dose >40 and 100 mg/ml following 12-h exposure compared with untreated and TGF-β1-treated cells. (F) TGF-β1 enhanced CYR61 expression and dexamethasone inhibited CYR61 expression and reversed TGF-β1-enhanced effects in NSCLC H1975 and H358 cells. **P<0.01 vs. the TGF-β1 group; ##P<0.01 vs. the control group. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. TGF-β1, transforming growth factor; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; CRY61, cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61.