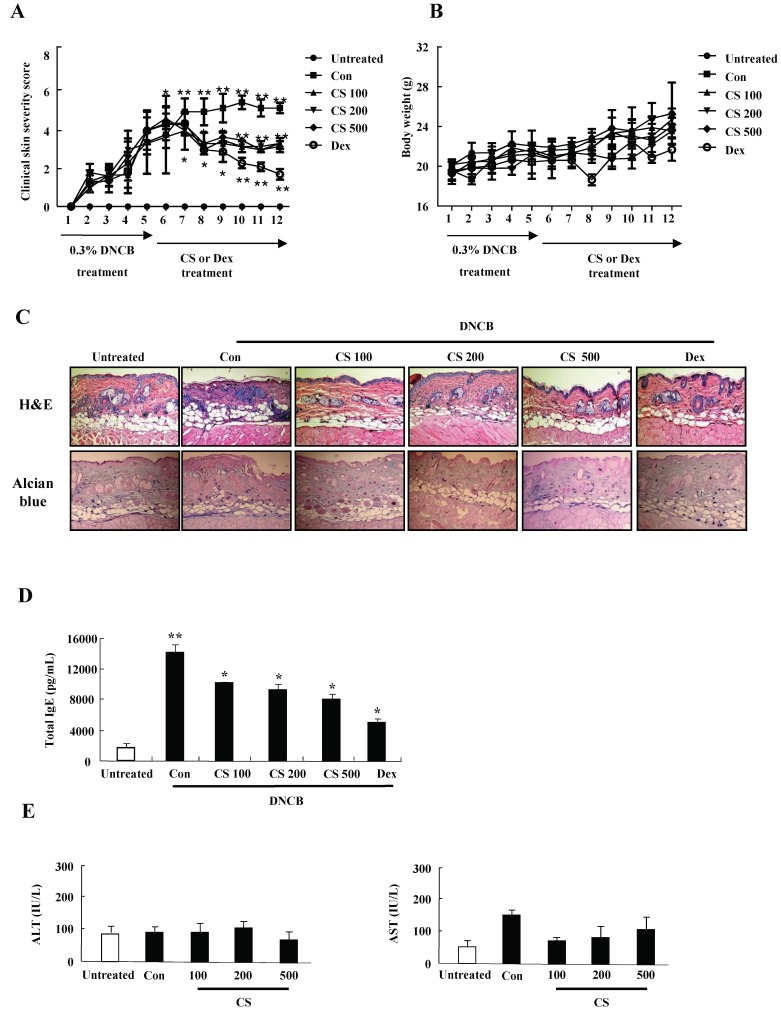
Figure 3.
CS extract reduces the severity of atopic-like lesions and decreases the histopathological features in DNCB-induced AD mice. The mice were divided into four groups: Untreated, control (Con), CS, and DEX. The control, CS, and DEX groups were dorsally administered with 1% DNCB and then dorsally treated with 0.3% DNCB. CS was administered orally at concentrations of 100, 200, and 500 µg/kg. DEX was administered orally at 5 mg/kg. (A) The severity of dermatitis was evaluted macroscopically in a blinded experiment. (B) Mouse mean body weight was measured by using an electric scale. Data are presented as a mean ± SD. (C) For histological analysis, the dorsal skin was fixed, embedded in paraffin, sectioned, stained with hematoxylin-eosin and alcian blue, and examined by using light microscopy (magnification, ×100). (D) Total serum IgE levels were measured by using sandwich ELISA kits. (E) The levels of AST and ALT were measured in the serum of NC/Nga mice by using the Reitman-Frankel method and ALT and AST assay kits. Data are presented as a mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 indicate a significant difference between the untreated and control groups or between the control and CS-treated groups.