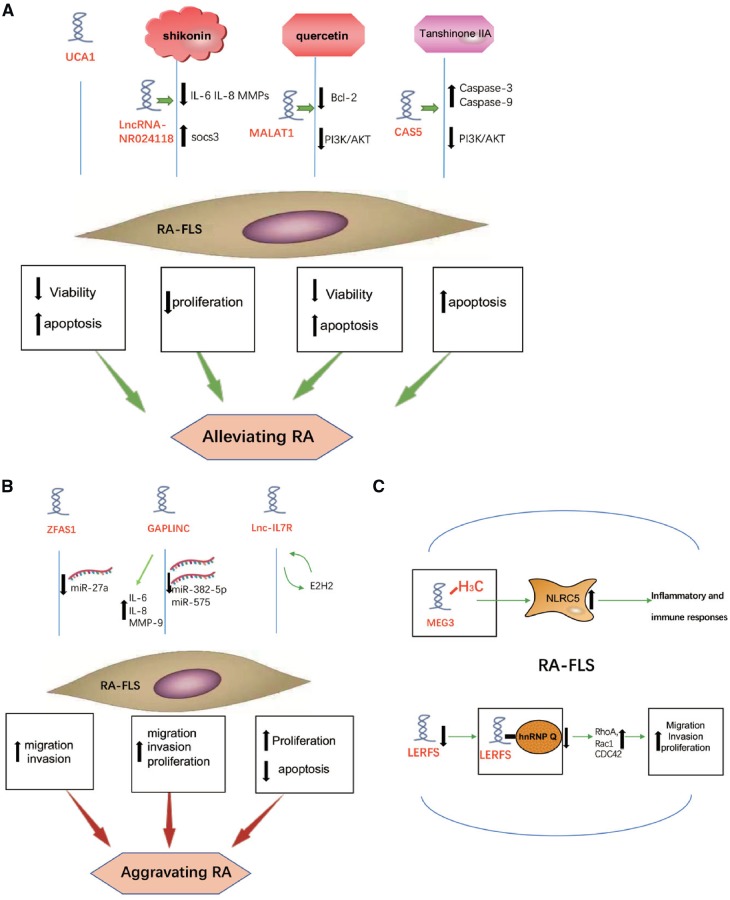
Fig. 1.
The role of lncRNAs in RA FLS
(A) UCA1 affects the pathogenesis of RA by reducing viability and inducing apoptosis of FLS. LncRNA-NR024118 is involved in the inhibition of shikonin on inflammation in FLS. MALAT1 is important to quercetin-induced apoptosis of FLS in RA. GAS5 increases after the Tan IIA treatment in RA FLS and GAS5 upregulates caspase-3 and caspase-9 levels and silences the PI3K/AKT pathway. (B) ZFAS1 promotes the migration and invasion of FLS by inhibiting miR-27a to aggravate RA. GAPLINC enhances inflammatory cytokine or proteinase expression. GAPLINC promotes RA FLS tumour-like features, including proliferation, migration and invasion by downregulating miR-382-5p and miR-575. Lnc-IL7R enhances RA FLS proliferation and suppresses its apoptosis to aggravate RA by interacting with EZH2. (C) In RA FLS, MEG3 promoter is methylated to decrease MEG3 expression, thus the increasing expression of NLRC5 participating in inflammatory and immune responses. Downregulated LERFS leads to a decrease of LERFS-hnRNP Q complex in RA FLS.