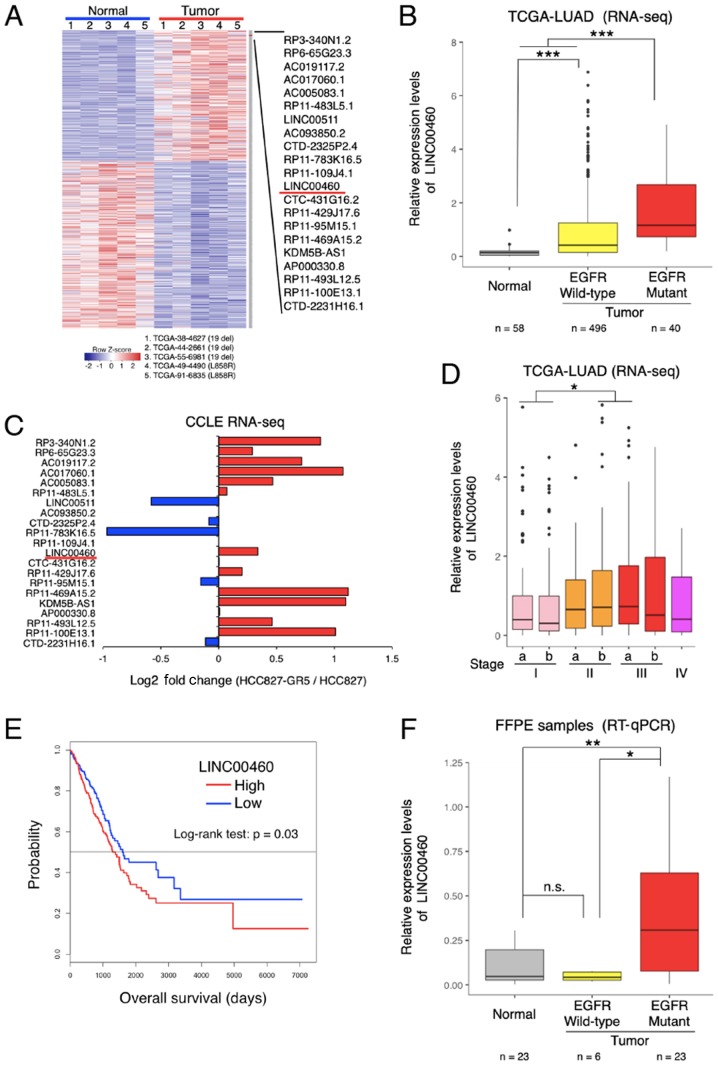
Figure 1.
Identification of lncRNAs dysregulated in EGFR-activating mutant lung adenocarcinoma. (A) The heatmap shows the expression levels of lncRNAs dysregulated in EGFR-activating mutant lung adenocarcinoma. lncRNAs were identified by RNA-seq analysis (TCGA-LUAD datasets). (B) Relative expression of LINC00460 transcripts in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and normal tissues using TCGA-LUAD RNA-seq datasets. Relative expression levels are presented as log2 (FPKM + 1). (C) Fold change in lncRNA expression in gefitinib-sensitive and -resistant HCC827 cells (HCC827 vs. HCC827-GR5). HCC827 is a gefitinib-sensitive lung adenocarcinoma cell line; HCC827-GR5 is a gefitinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cell line. lncRNAs were identified by using the log2 (RPKM + 1) value from RNA-seq datasets (CCLE). (D) LINC00460 expression in relation to clinical stage, based on the T-factor in lung adenocarcinoma, determined using RNA-seq and clinical data of TCGA-LUAD. (E) Kaplan-Meier curves for the overall survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. LINC00460 expression levels and clinical data were obtained from TCGA data. (F) LINC00460 expression in lung adenocarcinoma tissues with EGFR-activating mutations or wild-type EGFR, and in normal tissues. The data were determined by using RT-qPCR. GAPDH mRNA was used as an internal control. The level of statistical significance was set at a P-value <0.05 (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). n.s., not significant.