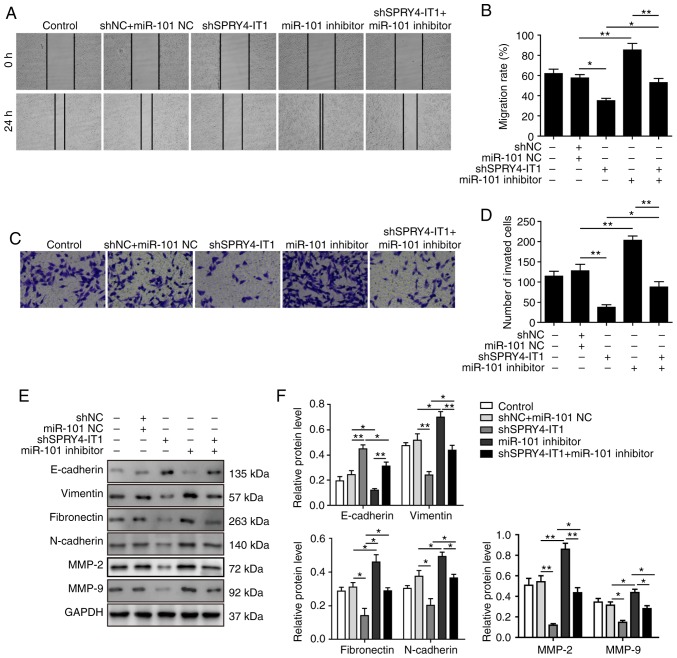
Figure 7.
miR-101 inhibitor reverses the shSPRY4-IT1-mediated suppression of cell migration and invasion in MG-63 cells. (A and B) SPRY4-IT1 knockdown significantly delayed wound closure, whereas miR-101 inhibitor increased wound closure. The shSPRY4-IT1-induced decrease in migratory rate was partially reversed by miR-101 inhibitor. (C and D) SPRY4-IT1 knockdown significantly reduced cell invasion, whereas miR-101 inhibitor increased cell invasion. miR-101 expression in SPRY4-IT1 knockdown cells reversed the effects of SPRY4-IT1 knockdown on cell invasion. (E and F) shSPRY4-IT1 increased E-cadherin protein expression levels, whereas vimentin, fibronectin, N-cadherin, MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels were decreased by SPRY4-IT1 knockdown, whereas cells transfected with miR-101 inhibitors exhibited the opposite changes in protein expression levels of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated proteins. Transfection of miR-101 inhibitor reversed the effects of shSPRY4-IT1 transfection. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. SPRY4-IT1, sprouty receptor tyrosine kinase signalling antagonist 4-intronic transcript 1; miR, microRNA; sh, short hairpin; NC, negative control; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase.