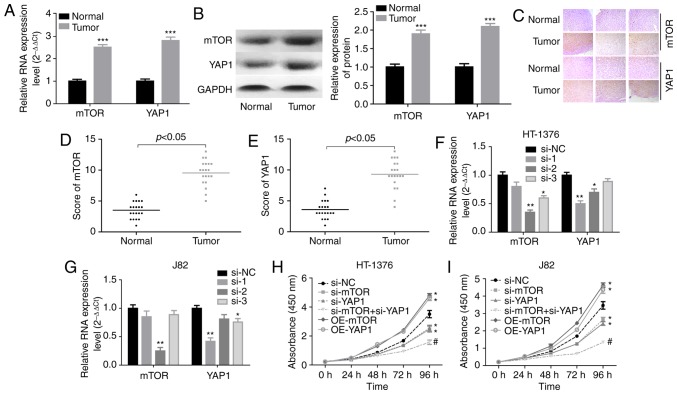
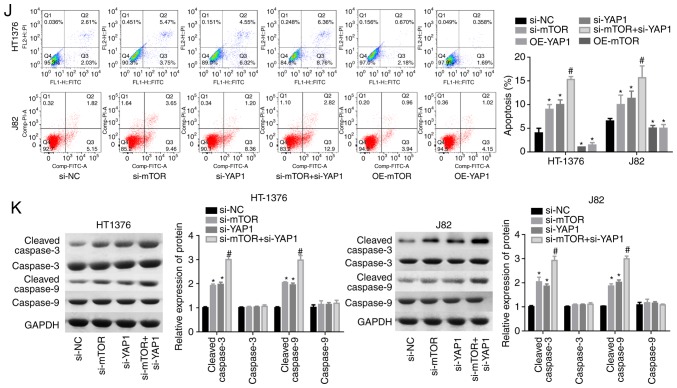
Figure 1.
Knockdown of YAP1 and mTOR inhibited the progression of bladder cancer. (A and B) RT-PCR and western blot assays were performed to test the expression of YAP1 and mTOR in bladder cancer and normal bladder tissues (***P<0.001). (C) Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the expression patterns of the YAP1 and mTOR proteins in three matched pairs of bladder cancer and normal bladder tissues (magnification, x200). (D and E) Immunohistochemistry scores of mTOR and YAP1 staining in 20 paired bladder cancer and adjacent normal tissues. (F and G) RT-PCR was used to analyze the knockdown efficien-cies of si-YAP1 and si-mTOR (*P<0.05, **P<0.01). (H and I) HT-1376 and J82 cells were transfected with si-NC, si-YAP1, si-mTOR or si-YAP1 + si-mTOR for 0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h; then, CCK-8 assay was performed to evaluate cell proliferation. (J) HT-1376 and J82 cells were transfected with si-NC, si-YAP1, si-mTOR or si-YAP1 + si-mTOR for 48 h; then, cells were collected for flow cytometry assay to detect cell apoptosis. (K) Western blotting was performed to detect the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as caspase 3/9 and cleaved-caspase3/9 after 48 h of cell transfection (H-K, vs. si-NC group, *P<0.05; vs. si-YAP1 group, #P<0.05; NC, negative control). YAP1, Yes-associated protein 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.